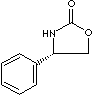
| (R)-4-PHENYL-2-OXAZOLIDINONE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 90319-52-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. | ||
| FORMULA | C9H9NO2 | |
| MOL WT. | 163.18 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY |
|
|
| DERIVATION |
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
R-4-Phenyl-oxazolidin-2-one; (R)-(-)-4-Phenyl-2-oxazolidinone; |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystalline powder |
|
| MELTING POINT | 129 - 134 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION |
||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. |
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
| Oxazolidinones, containing not only nitrogen but also oxygen atom in lactam ring, are used in developing novel drug especially antibiotics of low toxicity for the host but effective against penicillin-resistant pathogens. Chiral oxazolidinones are used in the enantioselective synthesis of beta-lactams and alpha-amino acids. End products can include asysmmetric single isomeric drugs of antitumor, anesthetic, antipasmodic, hepatotoxic, antiinflammatory or anti-HIV activity products. Chiral oxazolidinones have wide and effective chiral applications as chiral auxiliaries, building blocks and ligands. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
|
|
CHEMICAL PURITY |
98.5% min | |
|
OPTICAL PUIRTY |
99.0% min e.e. | |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: ,
Safety Phrases: 24-26 Optical Rotation: -47.5° ~ -48.5° (C=2 in Chloroform) |
||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF LACTONE |
||
|
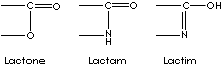
Lactone is an internal cyclic monoester (anhydride) derived from the hydroxyl and carboxyl radicals of gamma or delta hydroxy acids by the removal of a H2O between a carboxyl and a hydroxyl group in the same molecule; gamma-hydroxybutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactone and delta-hydroxydecanoic acid forms delta-decalactone spontaneously. In result, prefixes describe the ring size: beta- is for 4-membered ring), gamma- , 5-membered, and delta-, 6-membered ring. Lactam (a cyclic amide) is the nitrogen analog of lactone. Gamma-aminobutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactam (also called 2-pyrrolidinone). Lactim is the tautomeric enol form of lactam. Lactam structure, a heteroatomic cyclic amide compound, is an important part in antibiotics such as penicillin. These structures, cyclic esters and analogues, are active nucleuses in pharmacological activity and flavorings. Their good solvency properties also useful in industrial application. Lactams have big demand in artificial fibre industry. They are polymerizable and used as nylon precursors. |
||