| D-METHIONINOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 87206-44-8 |
|
| EINECS NO. | ||
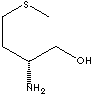
| FORMULA | C5H13NOS | |
| MOL WT. | 135.22 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | D-2-Amino-4-methylthiobutan-1-ol; | |
| D-2-Amino-4-metiltiobutan-1-ol; D-2-Amino-4-méthylthiobutane-1-ol; (R)-(+)-2-amino-4-methylthio-1-butanol; | ||
|
DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
clear crystals |
|
| MELTING POINT | 31 - 33 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 198 - 200 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.09 - 1.10 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION |
||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4511 | |
| FLASH POINT |
90 C |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. |
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
METHIONINE, an essential amino acid (sulfur-containing) that is not synthesized by the body and must be obtained from food. It contributes to supply mineral sulfur improving the tone and pliability of the skin, conditioning the hair and strengthens nails and protecting the cells from airborne pollutants. It contributes to the other compounds including S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), which participate in liabile methyl groups and sulfur to over 100 biochemical reactions for normal brain function, and L-Cysteine, which is a component of Glutathione, an important antioxidant molecule in the body. Methionine is also a transporter of the antioxidant mineral Selenium. METHIONINE occurs as two optical isomers, a dextro and a levo form. Chiral amino alcohol possessing both amine and alcohol is a structural motif for the compounds which have important biological and pharmacological functions within the body as inhibitor of aspartyl proteases, aldose reductase, b-amyloid peptide formation, and dopamine D4 antagonists. The chiral amino alcohol also exhibits anti-inflammatory, anesthetic, antipasmodic, hepatotoxic, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity,and anti-depressant activities. Chiral amino alcohols and their N-protected derivatives (Cbz, t-Boc, and Fmoc) are versatile building blocks, auxiliaries, ligand or resolving agent in asymmetric synthesis for biological and pharmaceutical researches. applications are present in the field of antitumor, anesthetic, antipasmodic, hepatotoxic, antiinflammatory or anti-HIV activities. Their derivatives include the forms of;
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear crystals |
|
|
CHEMICAL PURITY |
97.5% min | |
|
OPTICAL PURITY |
97.5% min | |
| OPTICAL ROTATION | +11.5° ~ +12.5° (C=neat) | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 22-24/26 | ||