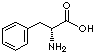
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLUBILITY IN SOLVENT
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid (a building block for proteins in the body), meaning the body needs it for health but cannot make it. You have to get it from food. Phenylalanine is found in three forms: L-phenylalanine, the natural form found in proteins; D-phenylalanine (a mirror image of L-phenylalanine that is made in a laboratory), and DL-phenylalanine, a combination of the two forms. The body changes phenylalanine into tyrosine, another amino acid that's needed to make proteins, brain chemicals including L-dopa, epinephrine, and norepinephrine, and thyroid hormones. Because norepinephrine affects mood, different forms of phenylalanine have been proposed to treat depression. Symptoms of phenylalanine deficiency include confusion, lack of energy, depression, decreased alertness, memory problems, and lack of appetite. On the other hand, a rare metabolic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU) occurs in people who are missing an enzyme that the body needs to use phenylalanine. That causes high levels of phenylalanine to build up. If it is not treated before 3 weeks of age, PKU can cause severe, irreversible mental retardation. In the United States, newborns are tested for PKU during the first 48 - 72 hours of life. People with PKU must eat a diet that avoids phenylalanine and take tyrosine supplements to have optimum brain development and growth. http://www.umm.edu
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenylalanine
Material Safety Data Sheet: http://www.chemcas.org/
chemistry/function:• L-phenylalanine is an essential amino acid that plays a key role in the biosynthesis of other amino acids, including L-tyrosine, and related biochemical processes involving the synthesis of several important neurotransmitters, principally L-dopa, dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Through a different metabolic pathway, L-phenylalanine can also be converted to phenylethylamine. Phenylethylamine is a naturally occurring substance in the brain that appears to elevate mood. Along with another amino acid, tryptophan, phenylalanine also governs the release of cholecystokinin, an intestinal hormone also known as CCK.
• D-phenylalanine, the mirror image of L-phenylalanine, does not occur naturally in the body. Further, it does not feed into the process of synthesizing L-tyrosine, L-dopa, or norepinephrine.
• DLPA is a mixture of the essential amino acid L-phenylalanine and its mirror image D-phenylalanine. DLPA does not occur naturally in the body. http://home.caregroup.org/
APPEARANCE
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
0.1% max
10ppm max
ASSAY