|
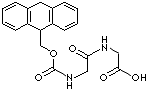
Fmoc-Gly-Gly-OH |
| Synonyms. Fmoc-Gly-Gly-OH; Fmoc-glycyl-glycine; Fmoc-(Gly)2-OH; N-alpha-(9-Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-glycinyl-glycin; N-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]glycyl-glycine ; N-9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonylglycylglycine 2-((2-(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)acetyl)amino)acetic acid; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
35665-38-4 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C19H18N2O5 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
354.36 |
|
H.S CODE |
2924.19.1150 |
|
SMILES |
C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(C3=CC=CC=C32)COC(=O)NCC(=O)NCC(=O)O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Dipeptide |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
1.34 |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Instability: 0; |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Dipeptide PubChem Compound Summary - Fmoc-Gly-Gly-OH http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Fmoc-Gly-Gly-OH http://www.peptideguide.com/
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white powder |
|
PURITY |
98.0% min (HPLC) |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Not known |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
|
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
|
|
P STATEMENTS |
|
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
24/25 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|