|
AMYLOPECTIN |
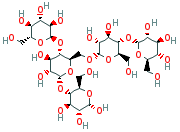
| Synonyms. Amylopectin; Waxy corn starch; Waxy maize starch; Waxy starch; Amioca; (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-((2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-6-(((2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-3 -((2R,3R,4S,5S,6R) -3,4,5-trihydroxy- 6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl)oxy-6- ((2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2- (hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl)oxyoxan -2-yl)methoxy)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl)oxy-6 -(hydroxymethyl) oxane-3,4,5-triol; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
9037-22-3 |
|
EINECS RN |
232-911-6 |
|
FORMULA |
|
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
|
|
H.S CODE |
3505.10.0040 |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Carbohydrate, Polysaccharide |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
A polydisperse highly branched polysaccharide derivative composed of chains of D-glucopyranose residues in α(1→4) glycosidic linkage. The chains are joined together by α(1→6) glycosidic linkages. A small number of α(1→3) glycosidic linkages and some 6-phosphate ester groups also may occur. The branches in amylopectin typically contain 24 to 30 glucose residues. ChEBI |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pK |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1, Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
USA.gov - Amylopectin Wikipedia Linking - Amylopectin Google Scholar Search - Amylopectin U.S. National Library of Medicine - Amylopectin PubChem Compound Summary - Amylopectin KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Amylopectin ChEBI (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/) - Amylopectin NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) - Amylopectin Human Metabolome Database - Amylopectin EPA - Substance Registry Services - Amylopectin AMYLOSE AND AMYLOPECTIN: Normal native starches consist of a mixture of 15-30 per cent. amylose and 70-85 per cent. amylopectin. Amylose approximately between 40 000 and 340 000, the chains containing 250 to 2000 anhydroglucose units. Amylopectin is considered to be composed of anhydroglucose chains with many branch points; the molecular weight may reach as high as 80 000 000 (Re. WHO). Amylose is an unbranched chain which is coiled in the shape of a helix. If iodine is added to a solution containing amylose molecules, the iodine inserts itself into the helix making it rigid. This changes the color of the starch mixture to blue or purple depending on the length of the amylose molecule. Amylopectin is a branching molecule which does not form a helical coil. Thus the iodine is not able to bind to the starch molecule. Amylose contributes to the gelling property of starch whereas amylopectin contributes high viscosity. This classic statement, however, may not be entirely valid. Both properties are used in the preparation of foods. International Starch Institute |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |
|
APPEARANCE |
white powder |
|
ASSAY |
93% min |
|
MOISTURE |
14% max |
|
pH |
5.8 ~ 8.2 |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION | |
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Not a dangerous substance. |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
Preserved in light-resistant and well-closed bottles |
|
|