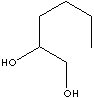
1,2-HEXANEDIOL
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
6920-22-5
H.S. CODE
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
Other RN: 87760-48-3
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
223 - 2240 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.442 ± 0.008
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - 1,2-Hexanediol
Wikipedia Linking - Diol
Google Scholar Search - 1,2-Hexanediol
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - 1,2-Hexanediol
PubChem Compound Summary - 1,2-Hexanediol
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - 1,2-Hexanediol
Material Safety Data Sheet - 1,2-Hexanediol
EPA - Substance Registry Services - 1,2-Hexanediol
http://journals.iucr.org/
.......1,2-Hexanediol solutions exhibited a strong attractive diol-diol interaction, a weak diol-diol attraction was found for 1,6-hexanediol and 1,2-pentanediol, and an extremely weak diol-diol attraction was found in 1,5-pentanediol solutions. The general tendencies are the following: aggregation is stronger as the length of the hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain increases and the 1,2-diols exhibit much stronger attraction then the 1,-diols. The temperature dependence of the aggregation is weak for the 1,2-diols but strong for the 1,-diols, indicating in the latter case the hydrophobic character of the interaction.......
Local:
Glycol: any of a class of organic chemicals characterized by having separate two hydroxyl (-OH) groups, contribute to high water solubility, hygroscopicity and reactivity with many organic compounds, on usually linear and aliphatic carbon chain. The general formula is CnH2n(OH)2 or
(CH2)n(OH)2. The broadened names
include diols, dihydric alcohols, and dihydroxy alcohols. Ethylene glycol,
HOCH2CH2OH, is the simplest
member of the glycol family. Mono-, di- and triethylene glycols are the first
three members of a homologous series of dihydroxy alcohols. Propylene glycol
prepared by hydrolysis of propylene oxide and widely used as an ingredient of
antifreeze and humectant in cosmetics is 1,2-propanediol indicating the two
hydroxyl group position at 1,2, while trimethylene glycol is 1,3-propanediol
with two hydroxyl group on the primary carbon atoms.
Diols contribute to high water solubility, hygroscopicity and reactivity with many organic compounds, on usually linear and aliphatic carbon chain. Alcohols are very weak acids as they lose H+ in the hydroxyl group. Alcohols undergoes dehydration reaction which means the elimination of water molecule replaced by a pi bond between two adjacent carbon atoms to form alkenes under heating in the presence of strong acids like hydrocloric acid or phosphoric acid. Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones respectively. Carboxylic acids are obtained from oxidation of aldehydes. Oxidation in organic chemistry can be considered to be the loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen and reduction to gain hydrogen or loss of oxygen. Tertiary alcohols do not react to give oxidation products as they have no H attached to the alcohol carbon. Alcohols undergoes important reactions called nucleophilic substitution in which an electron donor replaces a leaving group, generally conjugate bases of strong acids, as a covalent substitute of some atom. One of important reaction of alcohol is condensation. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Almost infinite esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. Alcohols are important solvents and chemical raw materials. Alcohols are intermediates for the production of target compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, plasticizers, surfactants, lubricants, ore floatation agents, pesticides, hydraulic fluids, and detergents.
| Hexanediol |
CAS RN |
EINECS |
| 1,2-Hexanediol | 6920-22-5 | 230-029-6 |
| 1,3-Hexanediol | 21531-91-9 |
|
| 1,5-Hexanediol | 928-40-5 | 213-171-3 |
| 1,6-Hexanediol | 629-11-8 | 211-074-0 |
| 2,4-Hexanediol | 19780-90-6 |
|
| 2,5-Hexanediol | 2935-44-6 | 220-910-3 |
| 3,4-Hexanediol | 922-17-8 | 213-073-0 |
APPEARANCE
PURITY
99.0% min
MOISTURE
0.5% max
TRANSPORTATION
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Skin irritation, Eye irritation, Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H335-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36
PRICE INFORMATION