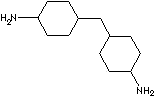
| 1,4-BIS(AMINOCYCLOHEXYL)METHANE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1761-71-3; 123203-35-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 217-168-8 | |
| FORMULA | CH2(C6H10NH2)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 210.36 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | p,p'-Diaminodicyclohexylmethane; Wandamin HM; | |
| 4,4'-Methylenebis(cyclohexylamine); Bis(4-aminocyclohexyl)methane; 4,4'-Diamino dicyclohexylmethane; 4,4'-Methylenebis(cyclohexanamine); 4,4'-Methylene bis(cyclohexylamine); 4,4'-Methylenedicyclohexanamine; 4,4'-Methylenedicyclohexane amine; 4,4'-Methylenedicyclohexylamine; Bis(p-aminocyclohexyl)methane; Methylene bis(4-aminocyclohexane); Di(p-aminocyclohexyl)methane; | ||
|
DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellowish semi-solid | |
| MELTING POINT |
35 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
339 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.96 - 0.98 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 153 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Diamines
are compounds which contain two amino groups. Both aliphatic (linear or branched
from short C-2 chain to fatty length ) and aromatic diamines are used as a
monomer to form copolymers like nylons, polyesters and polyurethanes for
characteristic properties. They can form a protein-like structure at both ends
of each monomer. The chain length characteristics with recurring amide groups
provide a variety physical properties and are further processed into various
applications including plastics, oil-modified and moisture-area types of
urethane coatings, polyamides for printing inks, dimer acids, textiles,
lubricant additive as scale and corrosion inhibitor, epoxy curing agent,
isocyanates, water treatment chemicals, biocides, and pharmaceutical
intermediates.
Cycloaliphatic diamines are used in urethane and epoxy coatings for light-stable, weather-resistant properties. It is used in water proofing and paving concreting. It is used in manufacturing diisocyanates and polyamides. Common cycloaliphatic diamines include isophorone diamine, 1,2-diaminocyclohexane, 1,4-bis(aminocyclohexyl)methane, 1,3-bis(aminomethyl)cyclohexane, bis(aminomethyl)norbornane. They are versatile intermediate to produce leather, rubber products, plastics, pesticides, dyes, and photo sensitive polymers. It is used in manufacturing diisocyanates and polyamides. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish semi-solid | |
|
PURITY |
99.0% min | |
|
WATER |
1.0% max | |
|
cis/cis (GC) |
18 - 25% | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 2928 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T+ N, Risk Phrases: 26-34-51/53, Safety Phrases: 26-28-36/37/39-45-61 | ||