| D-MANDELIC ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 611-71-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 210-276-6 | |
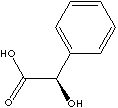
| FORMULA | C6H5CHOHCOOH | |
| MOL WT. | 152.15 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | (R)-a-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid; R-(-)-Mandelic acid; | |
| D-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid; ácido D-2-hidroxi-2-fenilacetico; Acide D-2-hydroxy-2-phénylacetique; (R)-2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetate; (R)-2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid; | ||
|
DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
White crystals | |
| MELTING POINT |
130 - 133 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Mandelic Acid, phenylglycollic acid, is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) which has a hydroxyl group on the carbon atom next to the acid group. If the hydroxy group is on the second carbon next to the acid group, it is called beta-hydroxy acid. Glycolic acid is the simplest AHA which has dual functionality of alcohol and acid in a low mole weight structure. Because of its small molecular weight and size, it has a better capability to penetrate skin. AHA is used extensively in cosmetics. It is known that it diminishes the lines on the skin and make skins look young by acting as a humectant to absorb moisture in air and by exfoliating action to break the bonds between dead skin cells. Mandelic Acid ( alpha-hydroxybenzeneacetic acid) is the smallest AHA among compounds which have aromatic group. It has an asymmetric carbon atom and thus has two chiral isomers; the dextro-, levo-. The D- and L-mandelic acid are enantiomers (also called enantiomorph; each molecule is asymmetrical and has the mirror image of the other) affect pharmaceutical activity. It is a white crystalline compound; melting at 118 C; partially soluble in water; freely soluble in isopropyl and ethyl alcohol; darkening upon exposure to light. Its structure provide the bacteriostatic property. It is excreted well in the urine. It is used as a antiseptic ingredient particularly against urinary tract infections. Mandelic acid and its derivatives are used to apply the dual activities as an antibacterial agent and as an antiaging agent (AHA activity) similar to glycolic acid. It is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of target molecules for other applications. Naturally occurring mandelic acid is found when amygdalin (a cyanogenetic glycoside found in many plants including bitter almond, apricot, and wild cherry) is spirit by hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid, while amygdalin is broken down into glucose, benzaldehyde, and prussic acid (hydrogen cyanide) in the presence of sulfuric acid. Mandelonitrile is the cyanohydrin from benzaldehyde. It is found in the millipede Apheloria corrugata as a defense mechanism. when Apheloria is about to be attacked, mandelonitrile decomposes enzymatically into benzaldehyde and a poison (hydrogen cyanide). Aamygdalin is known as laetrile which has been used as an anti-cancer drug. But it is known that it does not kill cancerous cells selectively. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
White crystals | |
| ASSAY |
99.0% min | |
|
SPECIFIC ROTATION |
-152° ~ -154° | |
| MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
| MELTING POINT |
130 - 133 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in fiber drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||