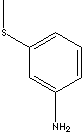
| m-THIOANISIDINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1783-81-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 217-232-5 | |
| FORMULA | CH3SC6H4NH2 | |
| MOL WT. | 139.22 | |
| H.S. CODE |
2930.90.2900 |
|
|
TOXICITY |
Bird - wild LD50 (Oral): 750mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | m-Methioaniline; 3-Methylmercaptoaniline; 3-Aminothioanisole; | |
| 3-(Methylthio)aniline; 3-(Metiltio)anilina; 3-(Méthylthio)aniline; 3-(Methylthio)benzenamine; 3-(Methylsulfanyl)aniline; 3-Aminothioanisole; | ||
|
SMILES |
c1(cc(ccc1)N)SC |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Thioether, Mercaptan, Aromatic Organo-sulfur Compound |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellow to brownish liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | 163 - 165 C at 16 mmHg | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.13 - 1.14 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 4870 mg/l | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| pKa | 4 (at 20 C) | |
| log Pow | 1.45 (Octanol-water) | |
| VAPOR PRESSURE | 0.012 (mmHg) | |
| HENRY'S LAW | 5.55E-08 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |
| OH RATE | 2.01E-10 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
110 C | |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Ether is any of a number of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom
joined with single bonds by two carbon atoms that are part of hydrocarbon
groups. The general formula is R-O-R', where R and R' are alkyl or aromatic
groups. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with
sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Ethers can be prepared from
alkyl halide reacted with metallic alkoxide (called Williamson synthesis).
Ethers are similar to alcohols but are generally less dense, less soluble in
water, and have lower boiling points. They are relatively unreactive, which
makes them valuable solvents. But ethers will be
cleaved at high temperatures by concentrated hydrogen halides. Ethers have relatively low boiling point
compare to alkanes as they don't form hydrogen bonds each other. Ethers are more
lipophilic than esters [R-C(=O)-O-R']or amides [RCO-NH2]. Ethers are widely used as solvents for various organic reactions because they
are relatively the least reactive among common organic compounds except alkanes
and fluorocarbons. The common reaction of ethers is cleavage of the C–O bond by
strong acids either in linear chain or cyclic structure. Ethers in which oxygen
is bonded to primary and secondary alkyl groups can form peroxide compounds in
the presence of gaseous oxygen due to two unpaired electrons in oxygen. Ethers can act as
Lewis bases in chemical reactions. Commonly, ethers are
named simply in listing the alkyl groups in alphabetical order or alkane order
such as ethyl methyl ether or methyl ethyl ether, which is methoxyethane in
IUPAC nomenclature ( the formula of "alkoxyalkane" ). When ether is a
parts of complex molecule or aromatic derivatives, it is described as an alkoxy
substituent such as methoxybenzene ( trivial name is anisole). The methoxy
prefix indicates the function methyl group joined by single bonds to an oxygen atom,
with the general formula -O-CH3. Cyclic ethers
have ring structure where the oxygen has become part of the ring. The term of
epoxide indicate three membered cyclic ether (also called oxirane) in which an
oxygen atom is joined to each of two carbon atoms that are already bonded to
each other; four
membered cyclic ether is called oxetane; five membered cyclic ether, furan (or
oxolane); six membered cyclic ether, pyran (also called oxane) respectively.
Their unhindered oxygen atom carries two unshared pairs of electrons - a
structure which favors the formation of coordination complexes and the solvation
of cations. Cyclic ethers are used as important solvents, as chemical
intermediate and as monomer for ring-opening polymerization. Crown Ether is a macrocyclic polyether whose structure contains
hydrogen, carbon and oxygen atoms. Each oxygen atoms are confined between two
carbon atoms and exhibits a conformation with a hole (accordingly called
"crown"). Anisole is one of the simplest aromatic compound to
which ether group is linked. But
it is different with aromatic compounds like furan where the oxygen is a part of
the ring. Anisole, C6H5OCH3
(methyl phenyl ether), is a clear liquid that is soluble in ether and
alcohol; insoluble in water; boiling point 155 C. Anisole and its derivatives
are used as solvents and in perfumery. Anisole can be obtained from anise seed.
Anisic acid, p-methoxybenzoic acid, is a part of cresol class antiseptic
compounds. It
is also used as an insect repellent and ovicide.
Anisole, anisic acid, and their derivatives are also widely used in
chemical reaction as intermediates to obtain target materials such as dyes,
pharmaceuticals, perfumes, photoinitiators and agrochemicals. Anisidines,
methoxyanilines, are used as intermediates for the synthesis of azo dyes,
pigments and other chemical compounds.
Mercaptan: any of a class of organosulfur compounds is similar to the alcohol and phenol but containing a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen atom. Compounds containing -SH as the principal group directly attached to carbon are named 'thiols'. In substitutive nomenclature their names are formed by adding '-thiol' as a suffix to the name of the parent compound. When -SH is not the principal group, the prefix 'mercapto-' is placed before the name of the parent compound to denote an unsubstituted -SH group. 'thio' is a chemical prefix indicates the replacement of an oxygen in an acid radical by sulfur with a negative valence of 2. Sulfur analog of alcohol is called thiol (or mercaptan), and ether analog is called sulfide. The first chemical contrast of thiols and sulfides with alcohols and ethers is acidity which is important in organic reactions. Thiols are stronger acids than relevant alcohols and phenols. Thiolate conjugate bases are easily formed, and are excellent nucleophiles in SN2 reactions of alkyl halides and tosylates. The nucleophilicity of sulfur is much greater than that of oxygen, resulting in a number of useful electrophilic substitution reaction that are rare by oxygen. For example, sulfides form (with alkyl halides) ternary sulfonium salts, in the same alkylattion of tert-amines quaternary ammonium salts, whereas ternary oxonium salts are prepared only under extream conditions. Without exception, sulfoxides, sulfinate salts and sulfite anion also alkylate on sulfur, despite of the partial negative formal charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on sulfur. The second character is the oxidation states of sulfur. Oxygen has only two oxidation states, whereas sulfur covers from –2 to +6 as follows:
One more sulfur compound's contrast with oxygen analog is in oxidation chemistry. Oxidation of sulfur compounds changes the oxidation state of sulfur rather than carbon, whereas, oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones changes the oxidation state of carbon not oxygen. Thiols is oxidized to S-S single bond (disufide) which is stronger than O–O bond in peroxide. Disufide forms sulfenyl chlorides (with chlorine in mild condition) or sulfonic acids under harder condition. Oxidation of sulfides with hydrogen peroxide (or peracids) yields sulfoxides and then to sulfones. A certain sulfoxide compound such as dimethyl sulfoxide can be used as an effective oxygen source in the oxidation reaction of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. DMSO easily is reduced to dimethyl sulfide and water is taken up by the electrophile. oxidation procedure is very mild and tolerates a variety of other functional groups, including those having oxidizable nitrogen and sulfur atoms. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish liquid | |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
WATER |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2810 | |
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-37/39 | ||