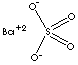| BARITE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 7727-43-7, 13462-86-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
231-784-4 |
|
| FORMULA | BaSO4 | |
| MOL WT. | 233.39 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | baryte; barytine; cawk; heavy spar; | |
| Barium sulfate; Sulfuric Acid, Barium Salt (1:1); | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white, blue, green, yellow or red shades crystal | |
| MELTING POINT | 1580 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 4.25 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | Not considered to be a fire hazard | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Barite is the most common barium mineral. It is a sulfate of barium found in nature as in tabular crystals, granules, or compact masses and has a high specific gravity (4.5). Its colors are variable (white, blue, green, yellow and red shades) and crystal system is orthorhombic. Barite occurs widely throughout the world. It often occurs in hydrothermal ore veins with lead, and zinc minerals. It is insoluble in water and practically insoluble in the most chemical reagents under ordinary conditions. Barite is used the chief source of barium and its chemical compounds. Ground barite is used as a filler in the manufacture of linoleum, oilcloth, paper and textile manufacturing, rubber, and plastics. Ground barite is used in the oil industry, e.g., as filtering and deodorizing agents in the refining of petroleum and, mixed with other materials, as drilling muds to protect the cutting bit while drilling. Bleached barite (white barite) is used in making paint as a white pigment. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
| BaSO4 |
90.0% min |
|
| SiO2 |
2.5% max |
|
| Fe2O3 |
1.5% max |
|
| SOLUBLES IN WATER |
1.0% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 22-24/25 |
||