| BIURET | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 108-19-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-559-0 | |
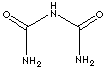
| FORMULA | NH2CONHCONH2 | |
| MOL WT. | 103.08 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Allophanic acid amide; Carbamoylurea; Carbamylurea; | |
| Allophanamide; Imidodicarbonic diamide; | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 187 - 190 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Biurate is a a condensation compound of urea, equivalent to two molecules of
urea less one of ammonia. It is a white needles; soluble in hot water; decompose
at 190 C. It is chelated with Cu2+ in alkaline solution to form an
intense violet-red color. The reaction also occurs with polypeptides, but not
with dipeptides or amino acids. It is used in colorimetric methods for total
proteins.
Carbamic acid is a compound of chemical formula H2NCOOH. But it exists only in the form of carbamate (its salt or ester), carbamide (amide) and carbamoyl (acyl radical). Carbamate structure inhibits cholinesterase and many insecticides and parasiticides contain carbamate fuctional group. It is highly toxic to human also. Heavy exposure to IT can cause carbamate poisoning. Natural carbamide (urea) can be found in protein metabolism in urine. Carbamoyl is the radical NH2CO-, also called carbamyl. It is involved in the biosynthesis of the pyrimidine ring. Carbamoyl compounds, such as salicylamides, are important for the preparation of pharmaceutical products, pesticides, dyes, and biosynthesis researches. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline crystals | |
| CONTENT |
97.0% min | |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
1.0% max | |
| MELTING POINT |
187 - 190 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs fiber drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 3260 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37, Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||
| BIOLOGICAL STAINS, INDICATORS | ||