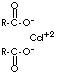|
CADMIUM STEARATE |
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. |
2223-93-0
|
|
| EINECS NO. | 218-743-6 | |
| FORMULA | (C17H35COO)2Cd | |
| MOL WT. | 679.35 | |
|
H.S CODE |
2915.70 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral Rat LD50: 1125mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Stearic acid cadmium salt; Kadmiumstearat; Cadmium distearate; | |
| Octadecanoic acid cadmium salt; Cadmium(II) n-octadecanoate; Cadmiumdistearat (German); Diestearato de cadmio (Spanish); Distéarate de cadmium (French); Cadmium octadecanoate; Cadmium soap; | ||
| SMILES | C(CCCCCCCCCCC)CCCCCC(=O)[O-].C(CCCCCCCCCCC)CCCCCC( =O)[O-].[Cd+2] | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Cadmium compound | |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 1 | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white powder | |
| MELTING POINT |
106 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 767 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.21 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY (AIR=1) | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 4, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
Local: APPLICATIONS: Cadmium organic salts, commercially cadmium stearate or cadmium laurate containing 1 - 16% cadmium, are the most effective stabilizer for polymers especially for PVC and its related products to develops good initial colour and clarity as well as to retard the degradation against heat and UV. These stabilizers allow high temperature process. These compounds are forbidden in food packaging applications. However, They are not replaced with other stabilizer for outdoor applications such as profiles, pipes, hoses and electrical insulation of the same effectiveness. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white powder | |
|
CADIMIUM CONTENT |
16.5
- 17.5%
|
|
|
MOISTURE |
1.0% max |
|
|
FREE ACID |
0.5% max |
|
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
99.0% min (150 mesh) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
25kgs in bag |
|
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 | |
| UN NO. | 2570 | |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CADMIUM |
||
Cadmium is a soft, ductile, tin-white transition
metallic
element belonging to group number 12 of periodic table; atomic number 48; atomic mass 112.411;
melting point 321.07°C; boiling point 767°C; specific gravity 8.65
g/cm3; Oxidation state
2; electronic configuration [Kr] 4d10 5s2. Cadmium is very resistant to corrosion.
It is reactive with strong oxidizing agents,
sulfur, selenium and tellurium. It loses luster in moist and is corroded by ammonia and sulfur dioxide.
Cadmium occurs
in the 0 and +2 oxidation states and forms many divalent
compounds which are reactive with potassium, magnesium, strong acids/bases,
and oxidizing agents. Cadmium is insoluble in water
but soluble in acids. Cadmium is a relatively rare metal;
closely related to zinc. Cadmium does not occur uncombined in nature;
occurs mainly in zinc mineral deposits and small amounts are found in copper and lead
ores. Greenockite (CdS) is the only cadmium
mineral. Cadmium is produced as a by-product in
electrolytic zinc refining. It is a metal capable of high polish
which provide the principle application in the electroplating of iron and steel.
It bears alloys with other metals, iron, copper, nickel, gold, silver, bismuth and aluminium,
for the low coefficient friction, corrosion resistance
and improving solderability and surface
conductivity. Cadmium alloys are used as a control absorber and shield in nuclear reactors. Some
cadmium compounds are used in batteries, semiconductors,
and photoconductive cells. Cadmium sulfide
photoconductive cell provides a high dark-light
resistance ratio. Cadmium silver oxide cell
is an alkaline-electrolyte cell which is used as a primary battery or a secondary-battery
than can be rechargeable. Cadmium telluride
is used in photoconductive cell which
can be operated at
ambient temperatures up to 400 C. It is used in solar cells and infrared, nuclear-radiation, and gamma-ray
detectors. Cadmium selenide is
a photoconductive and
semiconductor material used
in a cell
where a fast response time and high sensitivity to longer wavelengths of light
is required. Cadmium is used to produce luminous pigment
and fluorescent pigment which absorb light energy
and electromagnetic radiations and release visible light as energy of desired wavelength.
The principal cadmium pigments are consisted
of cadmium sulfides and sulfoselenides. Cadmium
sulfide is responsible for yellow color and cadmium selenide
is for red. cadmium pigments are used in the coloring of plastics and paints which hot
temperature resistance is required. Cadmium is used in the
production of various salts.
|
||