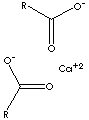| CALCIUM STEARATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1592-23-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 216-472-8 | |
| FORMULA | [CH3(CH2)16CO2]2Ca | |
| MOL WT. | 607.03 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2915.70 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Stearic acid calcium salt; Calcium octadecanoate; | |
| Octadecanoic acid, calcium salt; Calcium distearate; Calcium stearato (Italian); Calciumdistearat (German); Diestearato de calcio (Spanish); Distéarate de calcium (French); Other CAS RN: 7490-87-1, 8000-75-7, 37325-26-1, 105478-11-3, 169526-51-6, 177771-85-6 | ||
|
SMILES |
C(CCCCCCCCCCC)CCCCCC(=O)[O-].C(CCCCCCCCCCC)
CCCCCC(=O)[O-]. [Ca+2] |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Carboxylic Acid Salt |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white solid |
|
| MELTING POINT |
145 - 155 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.03 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS &GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Calcium Stearate is used as a stabilizer for plastics with co-stabilizer of Ba-Cd soap. It is also used as a plasticizer in plastic industry as well as in cosmetics. It is used as a flatting and sanding agent in lacquers, coatings & inks. It is applied in tablet manufacturing. It is used as a drying lubricant and dusting agent for rubbers. It is used as a catalyst in chemical synthesis. It is used as a waterproofing additive in concrete, rockwool, textiles and paper. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
White Powder |
|
| Ca CONTENT |
6.0 - 7.0% |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
145 - 155 C |
|
| FREE FATTY ACIDS |
0.5% max |
|
| FINENESS |
99.0% (325 mesh) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs, 1mt in bag in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF METALLIC SALTS OF FATTY ACIDS |
||
| Metallic salts of fatty acids (called soap) are primarily used as cleansing agent (mainly sodium- and potassium-) which their molecules attach readily to both polar molecules (of water) and non-polar molecules (of grease or oil). The long hydrocarbon chains are non-polar (and hydrophobic) repelled by water and the salt end molecules are ionic (and hydrophilic) water soluble. Soaps differ according to the type of fatty acid and length of the carbon chain and according to the alkali employed. Fatty acids with longer chains are insoluble. If sodium hydroxide is used as the alkali, hard soaps are formed; potassium hydroxide yields soft soaps. Soap salts are used as insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and algaecides. The lipophilic carbon chains infiltrate and destroy the lipoprotein matrix of the insect's cell membranes. Food grade soap salts are used also as general purpose food additives. Aluminum, calcium, magnesium, lead, zinc or other metals are used in place of sodium or potassium for soaps to be used in industry. Metallic salts of fatty acids are used as stabilizer and plasticizer in plastic industry as well as in cosmetics. They are used as flatting and sanding agents in lacquers, coatings & inks. They can be applied in tablet manufacturing. They are used as drying lubricants and dusting agents for rubbers. They are used as catalysts in chemical synthesis and emulsifiers for emulsion polymerization of synthetic rubber and resin which can be approved for use in food contact applications. They are used as waterproofing additives and ointments. | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FATTY ACID |
||
| Fatty Acids are aliphatic carboxylic acid with varying length hydrocarbon chains at one end of the chain joined to terminal carboxyl (-COOH) group at the other end. The general formula is CnH2n+1COOH or R-(CH2)n-COOH. Fatty acids are predominantly unbranched and those with even numbers of carbon atoms between 12 and 22 carbons long react with glycerol to form lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Fatty acids all have common names respectively like lauric (C12), MyrIstic (C14), palmitic (C16), stearic (C18), oleic (C18, unsaturated), and linoleic (C18, polyunsaturated) acids. The saturated fatty acids have no solid bonds, while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid has one solid bond (also described as olefinic) and polyunsaturated fatty acids like linolenic acid contain two or more solid bonds. Lauric acid (also called Dodecanoic acid) is the main acid in coconut oil (45 - 50 percent) and palm kernel oil (45 - 55 percent). Nutmeg butter is rich in myristic acid (also called Tetradecanoic acid ) which constitutes 60-75 percent of the fatty-acid content. Palmitic acid(also called Hexadecylic acid ) constitutes between 20 and 30 percent of most animal fats and is also an important constituent of most vegetable fats (35 - 45 percent of palm oil). Stearic acid ( also called Octadecanoic Acid) is nature's most common long-chain fatty acids, derived from animal and vegetable fats. It is widely used as a lubricant and as an additive in industrial preparations. It is used in the manufacture of metallic stearates, pharmaceuticals, soaps, cosmetics, and food packaging. It is also used as a softener, accelerator activator and dispersing agent in rubbers. Oleic acid (also called octadecenoic acid) is the most abundant of the unsaturated fatty acids in nature. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37, Safety Phrases: 22-24/25-26-28A | ||