PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
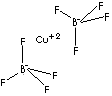
TOXICITY
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
blue crystals
Health hazard: 3, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Fluoroboric acid and the fluoroborates are commercially important to a
variety of industries. The acid is used in plating circuits, in metal finishing,
in the production of aluminum, and as an acid catalyst. Main group metal and
ammonium fluoroborates find use as fluxes, as catalysts, and in flame-retardant
manufacture. Transition- and other heavy-metal fluoroborate salts are used in
the plating industry and as catalysts. Properties and manufacture are
described.
http://ixian.ca/
Acid
Fluoborate Copper Processes Copper fluoborate is much more soluble
than copper sulfate. Therefore for high-current-density and high-speed
processes, the copper-ion concentration can be more than double
that obtainable in the sulfate baths. The fluoborate ion also helps
provide solubility and conductivity. But when compared with sulfate
baths, the fluoborate bath has less throwing power. The copper sulfate
bath is more widely used than the fluoborate because it is less
expensive. Also, many more additive systems have been developed
for copper-sulfate formulations. Copper fluoborate baths are more
hazardous to use and harder to waste treat than sulfate baths. And
as with the sulfate baths, the fluoborate solutions are very corrosive,
making careful design of plating equipment important. Chemistry
of copper fluoborate baths. Table VII shows the composition of a
typical acid copper fluoborate bath. If the fluoboric acid concentration
is too low (pH above 1.7), the deposit may be dull, dark, and brittle.
Add boric acid to stabilize the bath and to prevent the decomposition
of the fluoborate to fluoride. The anode film and its care in a
fluoborate bath are very similar to the requirements described for
the copper sulfate bath
Local: Fluoroboric acid is used in plating circuits; metal finishing; electropolishing of aluminium and its alloy; component of galvanic baths; organic synthesis as catalyst for alkylations and polymerisation; stabilisation of diazo salts; manufacturing of inorganic fluoroborate salts.
Inorganic fluoroborate salts are used as components of fluxing and plating, as catalysts, in flame-retardant manufacture, in metal treatment; grain refining agents; as active fillers in resin bonded abrasives; in electrolytic generation of boron, preparation of glazing frits.
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
Cu(BF4)2
44 - 46.0%
FREE ACID
1.0% max
SO4
1.2% max
SiO2
0.5% max
Cl
0.1% max
HEAVY METAL
10ppm max
50kg in drum
GHS
Danger
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302
+ H312 Harmful if swallowed or in contact with skin.
H314 Causes
severe skin burns and eye damage.
H332 Harmful if inhaled.
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P280
Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection.
P305
+ P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several
minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue
rinsing.
P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
![]() C
Corrosive
C
Corrosive
RISK PHRASES
20/21/22
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if
swallowed
34
Causes burns
SAFETY PHRASES
26
In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with
plenty of water and seek medical advice
36/37/39
Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face
protection
45
In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical
advice immediately (show label where possible)