|
SODIUM METASILICATE PENTAHYDRATE |
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 6834-92-0 (Anhydrous), 10213-79-3 (Pentahydrate), 13517-24-3 (Nonahydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 229-912-9 | |
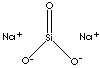
| FORMULA | SiO3Na2•5H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 212.74 | |
|
H.S.CODE |
2839.19 |
|
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 1153 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Metso Beads, Silicic acid, disodium salt; Sodium-m-Silicate; | |
| Orthosil; Disodium metasilicate; Disodium Monosilicate; Waterglass; Disodium trioxosilicate; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES (PENTAHYDRATE) |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white granule | |
| MELTING POINT |
|
|
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble in cold water. Hydrolyzes in hot water |
|
| pH | 12.3 - 12.5 (1% Solution) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | Not considered to be a fire hazard | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Detergents and soap, textile processing , pulp and paper, elastomers, disinfection agents, coatings, agriculture, ceramic industry. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white granules |
|
| SiO2 |
28.5 ± 1.0% |
|
| Na2O |
28.5 ± 1.0% |
|
| H2O |
45.5 ± 1.0% |
|
|
Fe |
100ppm max |
|
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
>1,6
mm: 2.0% max 1.6 - 1.2mm: 5.0 - 25.0%, 1.2 - 1.0mm: 15.0 - 35.0% 1.0 - 0.5mm: 35.0 - 55.0% 0.5 - 0.2mm: 5.0 - 25.0 % < 0.2mm: 2.0% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs, 1mt bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34-37, Safety Phrases: 13-24/25-36/37/39-45 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SODIUM SILICATE |
||
|
Sodium silicate, also called water glass or Soluble Glass, is any one of several compounds containing sodium oxide, Na2O, and silica, Si2O, or a mixture of sodium silicates varying ratios of SiO2 to Na2O, solids contents, and viscosity. Sodium Orthosilicate is Na4SiO4; Sodium Metasilicate is Na2SiO3; Sodium Disilicate is Na2Si2O5; Sodium Tetrasilicate is Na2Si4O9. All these compounds are colorless, transparent, glasslike substance available commercially as a powder or as a transparent, viscous solution in water.They can be dissolved in water to form a syrupy liquid. Some forms are slightly soluble, and some are almost insoluble; they are best dissolved by heating with water under pressure.The solutions are strongly alkaline.They are produced chiefly by fusing sand and sodium carbonate in various proportions. The use of sodium silicates is as a raw material for making silica gel. Also used as a detergent; as a cement for glass, pottery, and stoneware; for fireproofing paper, wood, cement, and other substances; for fixing pigments in paintings and cloth printing; and for preserving eggs. |
||