|
SULFUR | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 7704-34-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 231-722-6 | |
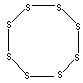
| FORMULA | S | |
| MOL WT. | 32.06 | |
|
H.S.CODE |
2802.00 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Brimstone; Sulphur | |
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellow crystals | |
| MELTING POINT |
112.8 C (rhombic) | |
| BOILING POINT |
445 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
2.07 (rhombic) | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Practically insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
8.9 | |
| AUTOIGNITION | 232 C | |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
FLASH POINT |
207 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Sulfur is a yellow non-metallic chemical element belonging to the Group VIa of the periodic table; symbol S; atomic number and weight 16, 32.06; melting at or about 112.8°C (rhombic), 119.0°C (monoclinic), 120°C (amorphous); boiling at or about 444.61 °C; specific gravity 2.07 (rhombic), 1.957 (monoclinic), 1.92 (amorphous) at 20 C; valence -2 (sulfide, S2-), +4 (sulfite, SO32-), and +6 (sulfate, SO42-). Sulfur is a brittle, pale yellow, odorless, tasteless solid, insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulfide (the amorphous form is not). It burns in air with a blue flame, forming sulfur dioxide, SO2. Solid sulfur occurs principally in several forms; the three most important being the rhombic, monoclinic (or prismatic), and Amorphous (or plastic) sulfur. The most sulfur is rhombic which has orthorhombic crystalline structure and is stable at room temperature. Monoclinic sulfur obtained when liquid sulfur is cooled slowly, consists of long, needlelike, nearly transparent crystals. It is stable between at 96 C, but it changes slowly to the rhombic form at room temperature. Amorphous sulfur obtained when hot molten sulfur is cooled suddenly is a dark, non-crystalline, sticky, elastic, gumlike mass. Sulfur is a chemically one of the most reactive of the elements and forms many compounds, both by itself (sulfides) and in combination with other elements. Sulfur forms compounds in oxidation states -2, +4, and +6. Sulfur combines with nearly all elements. Sulfur forms ring and chain structures as it is the second only to carbon in exhibiting catenation. Crystalline sulfur composed of molecules containing eight sulfur atoms seems to be made of rings. Amorphous sulfur has a helical structure with eight atoms per spiral. Elemental sulfur is used as a component of black gunpowder and fireproducts and phosphatic fertilizers. It is used in the vulcanization of rubber, as a fungicide and insecticide and in the treatment of skin diseases someyimes. The principal use of sulfur is in the preparation of its compounds. The most important sulphur compound is sulphuric acid, H2SO4, a toxic, corrosive, clear liquid used in the preparation of chemicals, fertilizers, and explosives, and in petroleum refining. More than 80% of sulfur is converted to sulfuric acid. One of the most familiar sulfur compounds is hydrogen sulfide,H2S, a colourless, flammable, extremely poisonous gas used in the preparation of metallic sulfides, phosphors, oil additives and for purification of hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. Sulfur forms inorganic sulfides with the most of metals. Sulfur forms sulfur dioxide, SO2, a toxic, irritating, colorless gas used as a solvent, in paper manufacture and as a chemical intermediate in artificial ice, and ore refining. Other important compounds include sulfur trioxide, thionyl chloride, the numerous sulfate compounds, halogen compounds phosphorus pentasulfide, carbon disulfide and sulfa drugs. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
AGRICULTURAL BRIMESTONE |
||
|
PASTIL |
4mm X 2 mm (Dia X Height) | |
|
SULFUR CONTENT |
90.0% min | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
|
SWELLING AGENT |
10.0% max | |
|
INDUSTRIAL BRIMESTONE |
||
|
PASTIL |
4mm X 2 mm (Dia X Height) | |
|
PURITY |
99.5% min | |
|
ASH |
0.1% max | |
|
ACIDITY |
0.05% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
|
CARBON |
0.05% max | |
|
INDUSTRIAL SULFUR LUMP |
||
|
SIZE |
100mm max | |
|
PURITY |
99.5% min | |
|
ASH |
0.1% max | |
|
ACIDITY |
0.05% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.1% max | |
|
SULFUR POWDER |
||
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
150 mesh (99.5% min) | |
|
PURITY |
99.5% min | |
|
ASH |
0.5% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
|
SULFUR DUST |
||
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
100 - 325 mesh | |
|
PURITY |
99.5% min | |
|
ASH |
0.1% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max | |
|
ACIDITY |
0.05% max | |
|
CARBON |
0.05% max | |
|
Fe |
0.001% max | |
|
SODIUM |
0.001% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs, 50kgs, 1mt in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 4.1 (Packing group:III) | |
| UN NO. | 1350 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
|
||