|
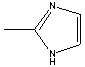
2-METHYLIMIDAZOLE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO |
693-98-1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 211-765-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C4H6N2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 82.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2933.29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 2-methyl-1H-imidazole; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
colorless to slightly yellow crystalline solod |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 142 - 143 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 267 - 268 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
soluble |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
155 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-Methylimidazole is used as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, textile auxiliaries, pigments and other organic chemicals. It is also used in polyurethane manufacturings and epoxy resins as a curing agent. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear to yellow solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ASSAY |
98.5% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
0.5% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing group:III) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 3263 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DESCRIPTION OF IMIDAZOLE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
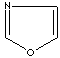
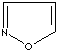
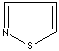
Imidazole is a heterocyclic compound of five-membered diunsaturated ring
structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms at nonadjacent
positions. The simplest member of the imidazole family is imidazole itself,
colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid with a weak aminelike odor; soluble
in water and alcohol, melts at 89 C, boils at 256 C. Imidazoles are poorly
soluble in water generally, but are dissolved in organic solvents, such as
chloroform, propylene glycol, and polyethoxylated castor oil. Imidazole ring is
found in histidine (an essential amino acid) and histamine, the decarboxylated
compound from histamine. Some imidazole compounds inhibit the biosynthesis of
ergosterol, required in cell membrane in fungal. They have antibacterial,
antifungal, antiprotozoal, and anthelmintic activity. Several distinct
phenylimidazoles are therapeutically useful antifungal agents against either
superficial or systemic infections. Thiabendazoles which have anthelmintic and
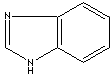
antifungal properties are imidazole class compounds. Benzimidazole is a dicyclic
compound having midazole ring fused to benzene. Benzimidazole structure is a
part of the nucleotide portion of vitamin B12 and the nucleus in some drugs such
as proton pump inhibitors and anthelmintic agents. Imidazole has two nitrogen
atoms.
The one is slightly acidic, while the other is basic. Imidazole and its
derivatives are widely used as intermediates in synthesis of organic target
compounds including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, photographic
chemicals, corrosion inhibitors, epoxy curing agents, adhesives and plastic
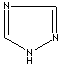
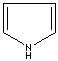
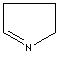
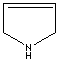
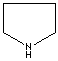
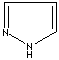
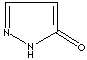
modifiers. Some imidazole analogues which contain nitrogen in five-membered ring
structure are:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||