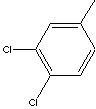
| 3,4-DICHLOROTOLUENE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 95-75-0 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 202-447-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C7H6Cl2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 161.03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 2400 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 1,2-Dichloro-4-methyl-benzene; 3,4-DCT; 3,4-二氯甲苯; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4-Dichloromethylbenzene; 3,4-Dichloro-1-methylbenzene; 3,4-DCT; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
ORGANOCHLORIDES / |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | -14 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 209 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.253 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
450 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
79 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
When substituted benzene molecules undergo electrophilic substitution reactions, substituents on a benzene ring can influence the reactivity. Activating substituents that activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack can alter the reaction rate or products by electronically or sterically affecting the interaction of the two reactants. deactivating substituents removes electron density from the benzene ring, making electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions slower and more difficult than benzene itself. For example, a hydroxy or methoxy substituent in phenol and anisole increases the rate of electrophilic substitution, while a nitro substituent decreases the ring's reactivity. Electron donating substituents activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack, and electron withdrawing substituents deactivate the ring, making it less reactive to electrophilic attack. The strongest activating substituents are the amino (-NH2) and hydroxyl (-OH) groups.
Activating substituents generally direct substitution to the ortho and para positions where substitutions must take place. With some exceptions, deactivating substituents direct to the meta position. Deactivating substituents which orient ortho and para- positions are the halogens (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I) and -CH2Cl, and -CH=CHNO2 When disubstituted benzene molecules undergo electrophilic substitution reactions, a new substituent is directed depends on the orientation of the existing substituents and their individual effects; whether the groups have cooperative or antagonistic directing effects. Ortho position is the most reactive towards electrophile due to the highest electron density ortho positions. But this increased reactivity is countervailed by steric hindrance between substituent and electrophile. A nucleophilic substitution is a substitution reaction which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide on an aromatic ring. This mechanism is called SNAr ( the two-step addition-elimination mechanism), where electron withdrawing substituents activate the ring towards nucleophilic attack. Addition-elimination reactions usually occur at sp2 or sp hybridized carbon atoms, in contrast to SN1 and SN2 at sp3. Chloro and bromobenzene reacts with the very strong base sodium amide (NaNH2) to give good yields of aniline. Other nucleophilic aromatic substitution mechanisms include benzyne mechanism and free radical (SRN1) mechanism. Common reactions of substituent groups on benzene ring include:
Dichlorotoluenes are clear volatile liquids; insoluble in water. These materials are in neutral, acidic or alkaline solution. They are used as high boiling point solvents and as intermediates for the synthesis of various organic chemicals of chlorinated-nitrated pesticides and medicinal products. Position isomers are:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ISOMER IMPURITY |
1.0% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 250kgs in drum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 22/36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 24/25/28A/37/45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||