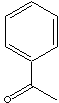
ACETOPHENONE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
TOXICITY
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
TSCA Flag T [Subject to the Section 4 test rule under TSCA]
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
198 - 204 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
77 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Acetophenone
PubChem Compound Summary - Acetophenone
Drug Bank - Acetophenone
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Acetophenone
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Acetophenone
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Acetophenone
Human Metabolome Database - Acetophenone
Local:
Acetophenone, the simplest aromatic ketone, is a clear liquid or crystals;
melting point 19 - 20 C; boiling point 202 C; very slightly soluble in water.
Commercial acetophenone can be obtained from benzene with
acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride by Friedel-Crafts process.
It can be also obtained by air oxidation
of
ethylbenzene, as a by-product of cumene
or from acrylonitrile. It
is used as a polymerization catalyst for the manufacture of olefins. It is used
as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and other organic
compounds. It also has been used as a drug to induce sleep. Its is used in tear
gas (especially as the form of chloro acetophenone) and warfare. It is used as
an solvent for plastics, resins, cellulose ethers, and esters. The dimer
(dipnone) is used as a plasticizer. Actophenone and its derivatives, having
additionally substituted saturated alkyls, oxygenated alkyl groups, thio groups,
additional aromatic groups, unsaturated aliphatic side chains, and other
functional groups, are ingredients of flavor & fragrance for in soaps,
detergents, cosmetics, and perfumes as well as in foods, beverages, and tobacco.
Members of aryl ketone
|
Systemic name |
Common name |
CAS RN |
|
Phenyl ethyl ketone |
Propiophenone | 93-55-0 |
|
Phenyl styryl ketone |
Chalcone | 94-41-7 |
|
Phenyl methyl ketone |
Acetophenone | 98-86-2 |
| Diphenyl ketone | Benzophenone | 119-61-9 |
| Phenyl phenacyl ketone | Dibenzoylmethane | 120-46-7 |
|
Phenyl o-tolyl ketone |
2-Methylbenzophenone | 131-58-8 |
|
Phenyl p-tolyl ketone |
4-Methyl benzophenone | 134-84-9 |
| Phenyl 2-thienyl ketone | Phenyl-2-thienylmethanone | 135-00-2 |
| Phenyl benzyl ketone | Deoxybenzoin | 451-40-1 |
| Phenyl 1-propenyl ketone | Crotonophenone | 495-41-0 |
| Phenyl propyl ketone | Butyrophenone | 495-40-9 |
| Phenyl methyl diketone | 1-Phenyl-1,2-propanedione | 579-07-7 |
|
Phenyl trans-styryl ketone |
trans-Chalcone | 614-47-1 |
|
Phenyl vinyl ketone |
2-Propenophenone | 768-03-6 |
| Phenyl phenethyl ketone | Dihydrochalcone | 1083-30-3 |
|
Phenyl xylyl ketone |
|
1322-78-7 |
|
Phenyl ethynyl ketone |
Propynophenone | 3623-15-2 |
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
0.5% max
Carbonyl groups are:
- Aldehydes (X and Y = H; X = H, Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Ketones (X and Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Carboxylic acids (X = OH, Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Esters (X = O-alkyl or aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Amides (X = NH, N-alkyl, or N-aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Acid halides
- Acid anhydrides
- Lactones
- Lactams
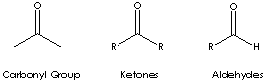
Ketone has the general formula RCOR' where the groups R and R' may be the same or different, or incorporated into a ring (R and R' are alkyl, aryl, or heterocyclic radicals). The simplest example, R and R´ are methyl group, is acetone (also called 2-propanone, CH3COCH3) which is one of the most important ketones used in industry (low molecular weight ketones are general purpose solvents.) In the IUPAC system, the suffix -one is used to describe ketone with the numbering of the carbon atom at the end that gives the lower number. For example, CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 is named 3-hexanone because the whole chain contains six carbon atoms and the oxygen is connected to the third carbon from the lower number. There are aromatic ketones of which acetophenone and bezophenone are examples. Ketones can be made by the oxidation of secondary alcohols and the destructive distillation of certain salts of organic acids. In addition to as polar solvents, ketones are important intermediates in the syntheses of organic compounds such as alkoxides, hydroxyalkynes, imines, alcohols (primary, secondary as well as tertiary), acetals, thioacetals, phosphine oxides, geminal diols, hydrazones, organic sulfite and cyanohydrins.
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Combustible liquid. Harmful if swallowed. Irritating to eyes. May cause skin and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: None known
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302-H319
P STATEMENTS
P301+ P312-P302 + P352-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
22-36
SAFETY PHRASES
26