PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
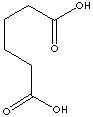
HOOC(CH2)4COOH
TOXICITY
SMILES
C(CCCCC(O)=O)(O)=O
CLASSIFICATION
Dicarboxylic acid, Food acidity regulator
EXTRA NOTES
FEMA No. 2011
Other RN: 1186514-28-2, 7486-39-7 (magnesium salt), 22322-28-7 (calcium salt), 23311-84-4 (hydrochloride salt), 25666-61-9 (potassium salt), 3385-41-9 (ammonium salt), 7486-38-6 (dihydrochloride salt)
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
337 C
3.45 (1%)
AUTOIGNITION
420 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
210 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
USA.gov - Adipic Acid
Wikipedia Linking - Adipic Acid
Google Scholar Search - Adipic Acid
U.S. National Library of Medicine - Adipic Acid
PubChem Compound Summary - Adipic Acid
IPCS INCHEM - Adipic Acid
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Adipic Acid
ChEBI (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/) - Adipic Acid
NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) - Adipic Acid
Material Safety Data Sheet - Adipic Acid
Human Metabolome Database - Adipic Acid
Adipic acid is an important inudstrial dicarboxylic acid with about 2.5 billion kilograms produced per year. It is used mainly in the production of nylon. It occurs relatively rarely in nature. It has a tart taste and is also used as an additive and gelling agent in jello or gelatins. It is also used in some calcium carbonate antacids to make them tart. Adipic acid has also been incorporated into controlled-release formulation matrix tablets to obtain pH-independent release for both weakly basic and weakly acidic drugs.
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Adipic Acid
EPA - Substance Registry Services - Adipic Acid
Local:
Adipic Acid (also called hexanedioic acid) is a white, crystalline compound of
C6 straight-chain dicarboxylic acid; slightly soluble in water and soluble in
alcohol and acetone. Almost all of the commercial adipic acid is produced from
cyclohexane through two sequent oxidation processes. The first oxidation is the reacting
of cyclohexane with oxygen in the presents of cobalt or manganese catalysts at a
temperature of 150 - 160 C, which produce cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Then,
the intermediates are further reacted with nitric acid and air with a catalyst
(copper or vanadium) or without nitric acid. Cyclohexane can be prepared by the
hydrogenation of benzene. There are other ways such as the reactions using
phenol, butadiene, and various fats as the starting material. Adipic acid
consumption is linked almost 90% to nylon production by the polycondensation
with hexamethylenediamine. Nylon, having a protein-like structure, is further
processed into fibers for applications in carpeting, automobile tire cord and
clothing. Adipic acid is used in manufacturing plasticizers and lubricants
components. It is used in making polyester polyols for polyurethane systems.
Food grade adipic acid is used as gelling aid, acidulant, leavening and
buffering agent. Adipic acid has two carboxylic acid, -COOH, groups, which can
yield two kinds of salts. Its derivatives, acyl halides, anhydrides, esters,
amides and nitriles, are used in making target products such as flavoring
agents, internal plasticizers, pesticides, dyes, textile treatment agents,
fungicides, and pharmaceuticals through further reactions of substitution,
catalytic reduction, metal hydride reduction, diborane reduction, keto formation
with organometallic reagents, electrophile bonding at oxygen, and condensation.
|
APPEARANCE
99.5% min
5 max
0.2 ppm max
ASH
7 ppm max
NITRATE
5 ppm max
WATER
0.2% max
- Plasticizer for polymers
- Biodegradable solvents and lubricants
- Engineering plastics
- Epoxy curing agent
- Adhesive and powder coating
- Corrosion inhibitor
- Perfumery and pharmaceutical
- Electrolyte
There are almost infinite esters obtained from carboxylic acids. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol. Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application selections.
|
C length (Straight) |
Product |
CAS # |
Melting Point |
Boiling Point |
|
C 2 |
Oxalic
Acid (Ethanedioic Acid) |
144-62-7 |
189 - 191 C |
Sublimes |
|
C 3 |
Malonic
Acid |
141-82-2 | 131 - 135 C |
Decomposes |
|
C 4 |
Succinic
Acid |
110-15-6 |
185 - 190 C |
235 C |
|
C 5 |
Glutaric
Acid |
110-94-1 |
95 - 99 C |
302 C |
|
C 6 |
Adipic
Acid |
124-04-9 |
151 - 153 C |
265 C at 100 mmHg |
|
C 7 |
Pimelic
Acid |
111-16-0 |
105 - 106 C |
212 C at 10 mmHg |
|
C 8 |
Suberic
Acid |
505-48-6 |
143 - 144 C |
230 C at 15 mmHg |
|
C 9 |
Azelaic
Acid |
123-99-9 |
100 - 103 C |
237 C at 15 mmHg |
|
C 10 |
Sebacic
Acid |
111-20-6 |
131 - 134 C |
294 at 100 mmHg |
|
C 11 |
Undecanedioic acid | 1852-04-6 |
109 - 110 C |
|
|
C 12 |
Dodecanedioic acid | 693-23-2 |
128 - 129 C |
245 C at 10 mmHg |
|
C 13 |
Brassylic acid (Tridecanedioic acid) |
505-52-2 |
112 - 114 C |
|
|
C 14 |
Tetradecanedioic acid | 821-38-5 |
126 - 128 C |
|
|
C 15 |
Pentadecanedioic acid | 1460-18-0 |
|
|
|
C 16 |
Thapsic acid (Hexadecanedioic acid) |
505-54-4 |
124 - 126 C |
|
|
C 18 |
Octadecanedioic acid |
871-70-5 |
|
|