|
DIETHANOL AMINE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 111-42-2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 203-868-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
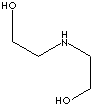
| FORMULA | (CH2CH2OH)2NH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 105.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2922.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 710 mg/kg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 2,2'-Iminobisethanol; Diethylolamine; DEA; Diolamine; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; N,N-Diethanolamine; Bis(hydroxyethyl)amine; 2,2'-Dihydroxydiethylamine; iminodiethanol; Diaethanolamin (German); Diethanolamin (Czech); 2,2'-iminobis-Ethanol; Di(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; Iminodiethanol; 2-[(2-Hydroxyethyl)amino]ethanol; 2,2'-Dihydroxydiethylamine; 2,2'-Iminobis[ethanol]; 2,2'-Iminodi-1-ethanol; 2,2'-Iminodiethanol; N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amine; Bis(hydroxyethyl)amine; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 28 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
268 - 267 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | miscible | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | 11.0 (0.1N aq sol.) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
662 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 ; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4770 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
130 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There are three ethanolamines called mono, di and tri-ethanolamine with
formula (CH2CH2OH)NH2,
(CH2CH2OH)2NH,
and (CH2CH2OH)3N
respectively. They are hygroscopic
viscous liquid or
semi-solid at room temperature. They are soluble in water, in alcohol and acetone, insoluble
in ether and benzene;
They are corrosive with a characteristic ammonia-like odor. their colors range from almost colorless to amber depending on purity. These substances decompose on heating and produce toxic and corrosive gases including nitrogen oxides. They are medium strongly basic and react with cellulose nitrate resulting in causing fire and explosion hazard. They react violently with strong acids and strong oxidants. Ethanolamines are produced from ethylene oxide reacted with ammonia. The principle product is monoethanolamine and secondary products of diethanolamine and triethanolamine are produced since ethylene oxide is reactive. They are the simplest members of the alkanolamine compounds. They have the physical and chemical characteristics of both alcohols and amines in one molecule. Ethanolamines stuctures are widely found in antihistamine drugs. In industrial field, monoethanolamine is an important raw material in the production of ethylenediamine. Ethanolamines are used as gas-scrubber in refinery and natural gas operations. They are widely used in the field of:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASSAY |
99.0% min |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
COLOR, APHA |
20 max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 220kgs in drum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing group: III) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 1719 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22-38-41-48/22, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||