| DIISOPROPANOLAMINE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 110-97-4 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 203-820-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
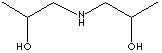
| FORMULA | [CH3CH(OH)CH2]2NH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 133.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2922.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Orl rat LD50: 4765 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine; DI(2-Hydroxy-n-propyl) amine; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,1'-imino-bis(2-propanol); DIPA; 2,2'-dihydroxy-dipropyl-amine; 1,1'-iminodipropan-2-ol; Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine; Bis(2-propanol)amine; Dipropyl-2,2'-dihydroxy-amine; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear to yellow solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 44.5 - 45.5 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
248 - 249 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.004 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble in methanol, acetone, ether | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | medium strong base | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 4.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
370 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | 126 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
There are three isopropanolamines called mono, di and tri-propanolamine with formula
with formula
CH3CH(OH)CH2NH2, CH3CH(OH)CH2]2NH, and CH3CH(OH)CH2]3N respectively. Monoisopropanolamine is a liquid at room temperature, while
diisopropanolamine and triisopropanolamine are white solids. Isopropanolamine is a clear to yellow,
corrossive, combustible liquid with a faint ammonia odor; boils at
159.9 C. It is soluble in water and very soluble in benzene and ether. Diisopropanolamine
is a clear to yellow hygroscopic crystalline lumps;
boils at 241 C, decomposes on heating producing toxic
nitrogen oxides. It is a medium strong base and
reacts violently with strong oxidants. It turns yellow when exposed to light and air.
Diisopropanolamine and triisopropanolamine
are commercially available in liquid grades contain
deionized water typically 15%. These liquid grades should
not be stored in the presence of aluminum due to the
possibility of excessive corrosion and potential chemical
reaction releasing flammable hydrogen gas at above 60
C. Isopropanolamines are used as an absorbent of acid
gases in the refinery of natural gas and purification of ammonia. They are used as an emulsifying agent
soluble in water and low alkalinity. They are used as a
crosslinking catalyst in the production of polyurethanes. They are used as a
component of insecticide, surfactants, rubber chemicals, corrosion inhibitors
and pigment dispersants.
Isopropanolamines have applications in the field of:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to yellow solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MIPA, TIPA IMPURITY |
1.5% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
0.5% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
85% AQ. SOLUTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to yellow liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
85.0% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MIPA, TIPA IMPURITY |
1.5% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
Balance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 190kgs in drum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||