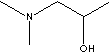| DIMEPRANOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 108-16-7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 203-556-4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | CH3CH(OH)CH2N(CH3)2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 103.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2922.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 1360 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 1-(Dimetilamino)propan-2-ol; 1-(Diméthylamino)propane-2-ol; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-Dimethylamino-2-propanol; 1-Dimethylaminopropan-2-ol; Dimethylamino-2-propanol; N,N-dimethylisopropanolamine; Dimethyl(2-hydroxypropyl)amine; N,N-(Dimethylamino)-2- propanol; N,N-Dimethyl-2-hydroxypropylamine; N,N-Dimethylisopropanolamine; 1-(Dimethylamino)-2-propanol; 1,1-(Dimethylamino)propanol-2; 1,1-Dimethylaminopropan-2-ol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear to light yellow liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | -40 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 121 - 127 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.835 - 0.845 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | miscible with water | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble in most organic solvents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4183 - 1.4203 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | 35 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
There are three isopropanolamines called mono, di and tri-propanolamine with formula
with formula
CH3CH(OH)CH2NH2, CH3CH(OH)CH2]2NH, and CH3CH(OH)CH2]3N respectively. Monoisopropanolamine is a liquid at room temperature, while
diisopropanolamine and triisopropanolamine are white solids. Isopropanolamine is a clear to yellow,
corrossive, combustible liquid with a faint ammonia odor; boils at
159.9 C. It is soluble in water and very soluble in benzene and ether. Diisopropanolamine
is a clear to yellow hygroscopic crystalline lumps;
boils at 241 C, decomposes on heating producing toxic
nitrogen oxides. It is a medium strong base and
reacts violently with strong oxidants. It turns yellow when exposed to light and air.
Diisopropanolamine and triisopropanolamine
are commercially available in liquid grades contain
deionized water typically 15%. These liquid grades should
not be stored in the presence of aluminum due to the
possibility of excessive corrosion and potential chemical
reaction releasing flammable hydrogen gas at above 60
C. Isopropanolamines are used as an absorbent of acid
gases in the refinery of natural gas and purification of ammonia. They are used as an emulsifying agent
soluble in water and low alkalinity. They are used as a
crosslinking catalyst in the production of polyurethanes. They are used as a
component of insecticide, surfactants, rubber chemicals, corrosion inhibitors
and pigment dispersants.
Isopropanolamines have applications in the field of:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to light yellow liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
COLOR, APHA |
50 max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
2.0% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: II) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 2734 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF AMINO ALCOHOL |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Amino alcohols which have the physical and chemical characteristics of both
alcohols and amines in one molecule . The amino alcohols are highly useful
materials for a wide variety of applications.
•Chemcial intermediate application
The amino alcohols are useful intermediates for a wide variety of synthesis. Many chemical reactions are common to the amino alcohols to form following examples; •Emulsifier applications Amino alcohols are used for production of efficient anionic emulsifiers and nonionic polyethylene emulsions. They appear in personal care products formulations and show better base strength, lower neutral equivalent, and lower volatility than traditional amine emulsifiers. Amino alcohols are used in personal-care products with the neutralization function of acid raw materials. They render resinous materials water-soluble. They provide base strength values with low odor levels, good water and alcohol solubility and color stability in cosmetics. •Coating application The difunctionality of amino alcohols makes them useful as raw materials in polymer applications in both water- and solvent-based to increase the solubility of other components and improve solution stability. They function as a pigment dispersion-aid dispersant to enhance the wetting and viscosity stability. The salts of the amino alcohols are also used in coating to improve the package stability. •Corrosion Inhibition application Amino Alcohols maintain a constant alkalinity in the boiling water flows and condensate not to form solid products which would impede line flow. This function is applied for corrosion Inhibits. They are widely employed in the preparation of water soluble cationic flocculants and ion exchange resins which adsorb solid and colloidal particles by electrostatic attraction. They are used for water treatment, metal treatmet and absorption of CO2 gas. •Catalyst application The salts of the amino alcohols like not only hydrochloride salts but also nitrate, sulfate, phosphate, and sulfonate salts can be used alone or in combination with other catalysts for balanced curing action with selected textile-resins. •Biochemical application In biological field, amino alcohol structure is widely found in many drugs especially antihistamines. Shingosine, the major base of the sphingolipids in mammals for signal transmission and cell recognition is an amino alcohol. Amino alcohol compounds are the starting materials in the preparation of beta-lactam antibiotics, humectant for foods and cosmetics, flavouring agents as well as many oral, injectable or topical pharmaceuticals. Amino alcohols are amine buffers used in a variety of medications. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||