| 1,3-DIMETHYLUREA | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 96-31-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-498-7 | |
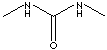
| FORMULA | CH3NHCONHCH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 88.11 | |
| H.S. CODE | 3102.10 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | N,N'-Dimethylurea; symmetric Dimethylurea; | |
| N,N'-Dimethylharnstoff (German); Urea, 1,3-dimethyl-; DMU; 1,3-Dimetilurea (Spanish); 1,3-Diméthylurée (French); | ||
|
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white flake | |
| MELTING POINT | 104 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
267 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.15 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | freely soluble | |
| pH |
| |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
400 C | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
| FLASH POINT |
157 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
|
1,3-Dimethylurea (DMU) is a solid in the form of white crystals with a faint ammonia-like odor It is soluble in water. It acts as a radical scavenger that protects isolated pancreatic islets from the effects of alloxan and dihydroxyfumarate exposure. Methyl amine and 1,3-dimethylurea are hydrolysis products of methyl isocyanate. It is used in manufacturing synthetic caffeine, resins and drugs. 1,3-Dimethylurea is used as a catalyst for condensation of methylamine with urea. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white flake | |
| PURITY |
95.0% max | |
| SOLIDIFICATION POINT |
102 C min | |
|
IRON |
5ppm max | |
|
HEAVY METAL |
20ppm max | |
|
WATER |
0.2% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||