| FORMALDEHYDE CYANOHYDRIN | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 107-16-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-469-1 | |
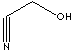
| FORMULA | OHCH2CN | |
| MOL WT. | 57.05 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2926.90 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Glycolonitrile; Cyanomethanol; Glycolic nitrile; | |
| Glyconitrile; Hydroxyacetonitrile; Hydroxyactonitrile; Hydroxymethylnitrile; 2-Hydroxyacetonitrile; 2-Hydroxyethanenitrile; Glykolonitril (German); Hydroxymethylkyanid; Glicolonitrilo (Spanish); Glycolonitrile (French); | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear to pale yellow liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | < -72 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | miscible | |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble: alcohol, ether, acetone, benzene; Insoluble: petroleum ether | |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
| pH |
2 - 3 (10% Sol.) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 4 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 2 | |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Cyanohydrins are organic compounds which contain both cyano and hydroxyl groups linked to the same carbon atom usually. Cyanohydrins are obtained from the reactions of aldehydes (or ketones) with hydrogen cyanide in base. They are versatile intermediates for the synthesis of organic compounds including amino nitriles; alpha-hydroxy acids, esters and amides; alpha-, beta- unsaturated acids, esters, nitriles as well as beta-aminoalcohols. Formaldehyde cyanohydrin is used to manufacture insecticides, pharmaceuticals and flavouring agents. It is used to prepare certain organic chemicals such as chelating agents. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
50% SOLUTION IN WATER |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear to pale yellow liquid | |
| CONTENT |
45 - 50% | |
| HYDROCYANIC ACID |
3.0% min | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 180kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing group: I) | |
| UN NO. | 3276 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T+, Risk Phrases: 26/27/28, Safety Phrases: 36/37/39-45 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF NITRILE | ||
|
Nitrile is an
organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing trivalent nitrogen)
which is attached to one carbon atom with the general formula RC��N. Their names
are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic acid' to the suffix,
'-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound) excluding the carbon
atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where the carbon atom in
the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O. Examples are
acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid. The prefix,
'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the presence of a
nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and organic derivatives
of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl derivatives
from the isomer, HN+��C-. Sodium cyanide,
NaCN; potassium cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or
prussic) acid, HCN are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides
resemble chlorides in many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are
reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids, oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons |
||