| SODIUM CHLOROACETATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 3926-62-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
223-498-3 | |
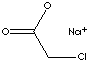
| FORMULA | CH2ClCOONa | |
| MOL WT. |
116.48 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 95 mg/kg. | |
| SYNONYMS | Chloroacetic acid, sodium salt; | |
| Natriumchloracetat (German); Cloroacetato de sodio (Spanish); Chloroacétate de sodium (French); SMA; Sodium monochloroacetate; Monochloroethanoic acid sodium salt; Monoxone; | ||
|
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 190 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble in ether, chloroform, benzene, and alcohol | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 4.0 | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. | |
|
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Monochloroacetic acid, chlorinated simplest carboxylic acid, has electron-withdrawing atoms on the next carbon to acid. Alha-chlorine makes monochloroacetic acid more acidic than acetic acid. Chloroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. The more electronegative atom presence tends to strengthen the acidic property. Trichloroacetic acid is stronger than monochloroacetic acid. Monochloroacetic acid and its derivatives are used as one of the first choice chemical intermediates for the production of;
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white powder | |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min | |
| SODIUM CHLORIDE | 0.5% max | |
|
FREE ACID |
0.2% max | |
|
IRON |
10ppm max | |
|
HEAVY METALS |
1ppm max | |
|
WATER |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2659 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T N, Risk Phrases: 25-38-50, Safety Phrases: 22-37-45-61 | ||