| CAS
NO. |
108-78-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
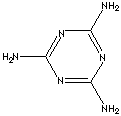
C3N3(NH2)3 |
| FORMULA |
203-615-4 |
| MOL
WT. |
126.12 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2933.61 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral, rat LD50: 3161 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Cymel; 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine;
cyanuramide; |
|
cyanuric triamide; triaminotriazine; 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine;
cyanurotriamide; Teoharn; Theoharn; Virset 656-4; cyanurotriamine; 2,4,6-triamino-s-triazine; s-triaminotriazine;
2,4,6-triamino sym-triazine;
1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)triimine; |
|
SMILES
|
Methylformate,
Condensed water |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
|
|
MELAMINE also
called Cyanuramide, or Triaminotriazine,
a colourless, is a crystalline substance belonging to the family of heterocyclic
organic compounds, which are used principally as a starting material for the
manufacture of synthetic resins. Melamine is manufactured by heating
dicyandiamide under pressure. Its most important reaction is the forming resinous compounds of high molecular weight,
with formaldehyde. These resins form under
the influence of heat but, once formed, are insoluble and infusible. Usually
formulated with fillers and pigments, they are molded into dishes, containers,
utensils, handles, and the like or used as laminating agents or coating
materials for wood, paper, and textiles. Formica and Melmac are well-known
trade names for products based on melamine resins. Butylated melamine resins,
made by incorporating butyl alcohol into the melamine-formaldehyde reaction
mixture, are fluids used as ingredients of paints and varnishes.
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white,
crystalline powder.
|
| MELTING POINT |
345
C (Decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.573 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
slightly |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
4.3 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
500
C
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary
conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Melamine-formaldehyde resins ,
Lamination , Adhesive agents, Tableware,
Flame retardant, Polyurethane foams, Paints, coating, paper, plastics,
Pigments, Thermosetting plastics |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
powder
|
| MELAMINE
|
99.9%
min |
| MOISTURE
|
0.05%
max
|
|
ASH
|
0.01%
max
|
|
pH
|
7.5 ~ 9.5
(5% sol.)
|
|
COLOR, APHA
|
30max
|
|
PARTICLE
DISTRIBUTION
|
90%(50 max)
100%(500 max)
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in bag and big bag |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
OF TRIAZINE COMPOUNDS
|
| Triazine is the chemical species of six-membered heterocyclic ring compound with
three nitrogens replacing carbon-hydrogen units in the benzene ring structure.
The names of the three isomers indicate which of the carbon-hydrogen units on
the benzene ring position of the molecule have been replaced by nitrogens,
called 1,2,3-triazine, 1,2,4-triazine, and 1,3,5-triazine respectively.
Symmetrical 1,3,5-triazine is the common. Triazines are prepared from
2-azidocyclopropene through thermal rearrangement (1,2,3-triazine), from
1,2-dicarbonyl compound with amidrazone by condensation reaction
(1,2,4-triazine) and from cyanic acid amide by trimerization (1,3,5-triazine).
Pyridine is the aromatic nitrogen heterocycle compound having only one nitrogen,
and diazines are with 2 nitrogen atoms and tetrazines are with 4 nitrogen atoms
on the benzene ring system. Triazines are weak base. Triazines have much weaker
resonance energy than benzene, so nucleophilic substitution is preferred than
electrophilic substitution. Triazines are basic structure of herbicides,
examples are amitole (CAS #: 61-82-5), atrazine (CAS #: 1912-24-9), cyanazine
(CAS #: 21725-46-2), simazine (CAS #: 122-34-9), trietazine (CAS #: 1912-26-1).
Large volume of triazines are used in the manufacture of resin modifiers such
as melamine and benzoguanamine. Melamine (1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine) is
reacted with formaldehyde to from a very durable thermoset resin. Benzoguanamine
(2,4-Diamino-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine) is used to increase thermoset properties
of alkyd, acrylic and formaldehyde resins. Triazines are also useful as
chromophore groups in colorants and Chlorine attached in Triazine compounds
undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions well with with hydroxyl groups in
cellulose fibres. Some triazine family compounds are used in pharmaceutical
industry as coupling agent for the synthesis of peptide in solid phase as well
as solution and as side chain of antibiotics. Triazine compounds are used in
formulating bactericide and fungicide. They are used as preservatives in oil
field applications. They are used as disinfectant, industrial deodorant and
biocide in water treatment. They are used as a bleaching agents. |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF FLAME RETARDANT AGENT |
|
Flame Retardant
are substances that can be
chemically inserted into the polymer molecule
or be physically blended in polymers
after polymerization to suppress, reduce, delay
or modify the propagation of a flame
through a plastic materials. There are several classes of flame retardants;
Halogenated Hydrocarbons (Chlorine and
Bromine containing compounds and reactive
flame retardants), Inorganic flame retardants
( Boron compounds, Antimony oxides,
Aluminium Hydroxide, molybdenum compounds,
zinc and magnesium oxides ), Phosphorous
containing compounds (Organic phosphate
esters, phosphates, halogenated phosphorus
compounds and inorganic phosphorus containing
salts).
Class of Flame Retardants
- Inorganic
- Metal
hydroxides
- Aluminium hydroxide
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Orthers
- Antimony compounds
- Antimony trioxide
- antimony pentoxide
- Sodium antimonate
- Others
- Boron compounds
- Boric acid
- Borax
- Zinc borate
- Others
- Other metal compounds
- Molybdenum compounds
- Titanium compounds
- Zirconium compounds
- Zinc compounds
- Zinc stannate
- Zinc hydroxy-stannate
- Others
- Others
- Phosphorus compounds
- Red phosphorus
- Ammonium polyphosphate
- Others
- Other inorganic flame
retardants
- ammonium sulfamate
- ammonium bromide
- Others
- Halogenated organic
- Brominated
- Tetrabromobisphenol A
- Decabromodiphenyl ether
- Octabromobiphenyl ether
- Tetrabromobiphenyl ether
- Hexabromocyclododecane
- Tribromophenol
- Bis(tribromophenoxy) ethane
- Tetrabromobisphenol A
polycarbonate oligomers
- Tetrabromobisphenol A
epoxy oligomers
- Others
- Chlorinated
- Chlorinated
paraffins
- Bis(hexachlorocyclopentadieno)cyclo-octane
- Others
- Organophosphoros
- Non-halogenated
compounds
- phosphate esters
- Ttrialkyl phosphates
- Triaryl
phosphates
- Aryl-alkyl phosphates
- Others
- polyols
- phosphonium
derivatives
- phosphonates
- Others
- Halogenated phosphates
- Tris(1-chloro-
2-propyl) phosphate
- Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate
- Tris(2,3-dibromopropyl)phosphate
- Others
- Nitrogen-based
- Polyurethanes
- Polyamides
- Melamine and
its salts
- Guanidine
compounds
- Others
|
