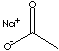
| SODIUM
ACETATE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 127-09-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 204-823-8 | |
| FORMULA | CH3COONa | |
| MOL WT. | 82.03 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2915.22 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3530 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Acetic acid, sodium salt; Acetic acid, sodium salt (1:1); | |
| Sodium Ethanoate; Acetate De Sodium; Natrium Aceticum; Natriumacetat (German); Sodii Acetas; Acetato de sodio (Spanish); Acétate de sodium (French); | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white hygroscopic crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 324 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.45 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
| pH |
8.9 |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | 2.83 | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
611 C |
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Sodium Acetate, sodium salt of acetic acid, is a white or colourless crystalline compound, prepared by the reaction of acetic acid with sodium carbonate or with sodium hydroxide. There are commercially anhydrous salt or trihydrate form losing water at 58 C. Both are soluble in water and in ethoxyethane, and slightly soluble in ethanol. Sodium Acetate is a salt of a strong base and a weak acid providing the application to be used as buffers in petroleum production and drilling muds, in food preservations, and in electroplating. It is used as a retardant in elastomer industry. It is used in tanning to effect a more even and rapid penetration of the tan in the leather industry. It is also used as a mordant in dyeing processes. Sodium Acetate is an intermediate to manufacture organic compounds like dyes, pigments, pharmaceuticals, cinnamic acid. It is also used in soap industry and purification of glucose. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
| ANHYDROUS TECHNICAL GRADE | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white odourless powder | |
| PURITY | 99.0% min | |
| INSOLUBLE MATTERS |
0.01% max |
|
| CHLORIDE |
0.01% max |
|
| CALCIUM |
0.1% max |
|
| POTASSIUM |
0.1% max |
|
| SULFATE |
0.1% max |
|
|
IRON |
5ppm max |
|
| HEAVY METAL(as Pb) |
5ppm max |
|
| TRIHYDRATE TECHNICAL GRADE | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white pr colorless crystals | |
| PURITY | 58.0 - 60.0% | |
|
FREE ALKALI |
0.03% max |
|
| INSOLUBLE MATTERS |
0.03% max |
|
| CHLORIDE |
0.04% max |
|
| PHOSPHATE |
0.1% max |
|
| SULFATE |
0.02% max |
|
|
IRON |
5ppm max |
|
| HEAVY METAL(as Pb) |
5ppm max |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 25kgs, 50kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 24/25 |
||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BUFFER |
||
|
Buffer is a
substance, generally a solution, that can keep its pH constant, despite the
addition of strong acids or strong bases and external influences of temperature,
pressure, volume, redox potential. Buffer prevents change in the concentration
of another chemical substance, e.g., proton donor and acceptor systems that
prevent marked changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH). Many acid-base
reactions take place in living organisms. However, for organisms to perform
certain vital functions, the body fluids associated with these functions must
maintain a constant pH. For example, blood must maintain a pH of close to 7.4 in
order to carry oxygen from the lungs to cells; blood is therefore a powerful
buffer. The commonest buffer in chemical solution systems is the acid-base
buffer.
|
||