PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
TOXICITY
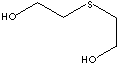
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
7
REFRACTIVE INDEX
160 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Thiodiglycol provides versatile solvency characteristics with both polar and non-polar properties. It is used as a solvent in dyeing textile and coating ways. It is used as a building block to produce corp protection products, dispersants, fibers, plasticizer, rubber accelerator, pesticides, dyes, and other organic compounds. It is used as a chain transfer agent in the manufacture of polymer.
Sulfate (also spelled sulphates in Euorpe) is any chemical compound related to sulfuric acid, formed by replacing one or both of the hydrogens with a metal or a radical. Sulfite is any salt of sulfurous acid, chemical species H2SO3, which is formed in aqueous solutions of sulfur dioxide. Sulfurous acid is a clear liquid with a strong sulfur aroma. Sulfide is a compound having one or more sulfur atoms in which the sulfur is connected directly to a carbon, metal, or other nonoxygen atom; for example, sodium sulfide, Na2S. Sulfur compounds are used in the synthesis of medicine and chemicals, manufacture of wood, pulp and paper. They are used in winemaking, brewing, food preservation, metallurgy, engraving process, ore flotation, additive in making steel, bleaching, metal treatment and as an analytic reagent.
The first chemical contrast of thiols and sulfides with alcohols and ethers is acidity which is important in organic reactions. Thiols are stronger acids than relevant alcohols and phenols.Thiolate conjugate bases are easily formed, and are excellent nucleophiles in SN2 reactions of alkyl halides and tosylates. The nucleophilicity of sulfur is much greater than that of oxygen, resulting in a number of useful electrophilic substitution reaction that are rare by oxygen. For example, sulfides form (with alkyl halides) ternary sulfonium salts, in the same alkylattion of tert-amines quaternary ammonium salts, whereas ternary oxonium salts are prepared only under extream conditions. Without exception, sulfoxides, sulfinate salts and sulfite anion also alkylate on sulfur, despite of the partial negative formal charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on sulfur. The second character is the oxidation states of sulfur. Oxygen has only two oxidation states, whereas sulfur covers from –2 to +6 as follows:
- -2: Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), sulfides, sulfonium ions
- -1: disulfides
- 0: S elemental, sulfoxides, sulfenic acids
- +2: sulfones, sulfinic acids
- +4: sulfonic acids, sulfite esters
- +6: sulfate esters
Information for glycol.
APPEARANCE
PURITY
98.5% min
WATER
0.3% max
COLOR, APHA
50 max
Thiol (also called Mercaptan), any of a class of organic chemical compounds, is similar to the alcohols and phenols but containing a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen atom. Compounds containing -SH as the principal group directly attached to carbon are named 'thiols'. In substitutive nomenclature their names are formed by adding '-thiol' as a suffix to the name of the parent compound. When -SH is not the principal group, the prefix 'mercapto-' is placed before the name of the parent compound to denote an unsubstituted -SH group.