o-CHLOROPHENOL
|
|
PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION
|
| CAS
NO. |
95-57-8 |
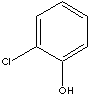
|
| EINECS
NO. |
202-433-2 |
| FORMULA |
C6H4Cl(OH) |
| MOL
WT. |
128.56 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2908.10 |
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
1-Chloro-2-hydroxybenzene; 2-Chlorophenol;
o-Chlorophenic acid; |
|
2-Hydroxychlorobenzene; 2-Chlorophenolate;
o-Chlorphenol (German); P-Chlorfenol (Czech); |
|
SMILES
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF CHLOROPHENOL COMPOUNDS |
Chlorophenols are organic halogen compounds of cyclic aromatics formed by
replacing hydrogen atoms in phenol by 1-5 atoms of chlorine. There are 19
compounds of chlorophenols of three mono-, six isomeric substances each of di-,
tri-, as well as three isomeric substances tetra-, and fully chlorinated
pentachlorophenol.
- 2-MONOCHLOROPHENOL
(CAS RN: 95-57-8)
- 3-MONOCHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN:
108-43-0)
- 4-MONOCHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 106-48-9)
- 2,3-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS
RN: 576-24-9)
- 2,4-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN:
120-83-2)
- 2,5-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 583-78-8)
- 2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS
RN: 87-65-0 )
- 3,4-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 95-77-2
)
- 3,5-DICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 591-35-5)
- 2,3,4-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 15950-66-0 )
- 2,3,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 933-78-8)
- 2,3,6-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 933-75-5)
- 2,4,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS
RN: 95-95-4)
- 2,4,6-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 88-06-2)
- 3,4,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 609-19-8)
- 2,3,4,5-TETRACHLOROPHENOL
(CAS RN: 4901-51-3)
- 2,3,4,6-TETRACHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 58-90-2)
- 2,3,5,6-TETRACHLOROPHENOL (CAS RN: 935-95-5)
- PENTACHLOROPHENOL (CAS
RN: 87-86-5)
Chlorinated phenol compounds are solids at room temperature,
except 2-Monochlorophenol which melts at 8 C. They are toxic copounds. But
the toxic property accounts for many of their uses. They are used as bactericides, fungicides and
preservatives. The water solubility of chlorophenols is low. Most chlorophenols
are commercially applied in the form of a chlorophenol-organic solvent
formulation. The salt forms are useful in case of particularly tri- and
tetrachlorophenols since salt forms are more soluble in water. Chlorinated
phenols are weakly acidic, more acidic with more chlorinated. The octanol/water
partition coefficients increases as chlorination increases. The taste and odour
thresholds are quite low. Chlorophenols are prepared by the alkaline hydrolysis
of the appropriate chlorobenzenes or by the direct stepwise chlorination
reaction of phenol or lower chlorinated phenols at a high temperature. Genrally,
higher chlorinated phenols and their salt forms are used in wood preservation
industry and in surface treatments for fresh-cut logs and lumber against
sapstain fungi and mould. The lower chlorophenols serve as intermediates in the
production of higher chlorophenols and various pesticides. 2-Chlorophenol is
used for higher to 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol pentachlorophenol.
4-Chlorophenol is a starting material for making germicides such as
2-Benzyl-4-chlorophenol; it can also be converted to an analgesic of
acetophenetidin. 2,4-Dichlorophenol with formaldehyde forms methylenebis
compounds used as a mothproofing agent, an antiseptic, and a seed disinfectant.
2,4-Dichlorophenol, with chloroacetic acid, forms 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
(2,4-D), used as a selective weed-killer, systemic herbicide and defoliant, also
used to increase the latex output of old rubber trees and in fruit drop control.
2,4-Dichloropheno, with formaldehyde, forms methylenebis compounds used as a
mothproofing agent, an antiseptic, and a seed disinfectant; 2,4-dichlorophenol,
with chloroacetic acid, forms 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) used as a
selective weed-killer, systemic herbicide and defoliant, also used to increase
the latex output of old rubber trees and in fruit drop control.
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is used as a bactericide and fungicide. The 2,4,5-isomer
has similar applications and also can be converted into hexachlorophene or
thiobis(trichlorophenol) used as germicides in soap; into dimethyl
trichlorophenyl phosphorothioate, a systemic agent effective against grubs in
cattle; into 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) or
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxypropionic acid (2,4,5-TCPPA), both widely used as weed
killers. Tetrachlorophenol is an insecticide and a bactericide and is used as a
preservative for latex, wood, and leather. Pentachlorophenol is a disinfectant,
a fungicide, and the most heavily used preservative for wood. It is primarily
used to protect timber from fungal rot and wood-boring insects, but the
technical material may also be extensively used in cooling towers of electric
plants, as additives to adhesives based on starch and vegetable and animal
protein, in shingles, brick walls, concrete blocks, insulation, pipe sealant
compounds, photographic solutions, and textiles and in drilling mud in the
petroleum industry.
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
to light yellow liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
6
-8 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
175
- 176 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.24 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly soluble |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
|
| pH |
Weakly acidic |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 |
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
63
C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
DESCRIPTION
AND APPLICATIONS
|
|
o-Chlorophenol is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pesticides, medicines, phenolic resins, dyes, aroma compounds and
other organic chemicals. It is used as a solvent for extracting sulfur and
nitrogen compounds from coal.
When substituted benzene molecules undergo electrophilic substitution reactions,
substituents on a benzene ring can influence the reactivity.
Activating
substituents that activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic
attack can alter the reaction rate or products by
electronically or sterically affecting the interaction of the two reactants.
deactivating substituents removes electron density from the benzene ring, making
electrophilic aromatic
substitution reactions slower and more difficult than benzene itself. For example, a hydroxy or methoxy substituent in
phenol and anisole increases the rate of
electrophilic substitution, while a nitro
substituent decreases the ring's reactivity. Electron donating
substituents activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic
attack, and electron withdrawing substituents deactivate the ring, making it less reactive to electrophilic attack.
The strongest activating substituents are the amino
(-NH2) and hydroxyl (-OH) groups.
|
Reactivity Effects |
Activating substituents |
Deactivating substituents |
|
Strong |
-NH2,
-NHR, -NR2,
-OH, -O-
|
-NO2,
-NR3+,
-CF3, CCl3
|
|
Moderate |
-NHCOCH3,
-NHCOR, -OCH3,-OR
|
-CN,
-SO3H,
-COOH, -COOR, -COH, -COR
|
|
Weak |
-CH3,
-C2H5,
-R, -C6H5
|
-F,
-Cl, -Br, -I
|
Toluene, aniline and phenol
are activated aromatic compounds. Examples of deactivated aromatic compounds
are nitrobenzene, benzaldehyde and halogenated benzenes.
Activating substituents
generally direct substitution to the ortho and para positions
where substitutions must
take place. With some
exceptions, deactivating substituents direct to the meta position. Deactivating substituents
which orient ortho
and para- positions are the halogens (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I) and -CH2Cl,
and -CH=CHNO2
When disubstituted benzene molecules undergo electrophilic substitution reactions,
a new substituent is directed depends on the orientation of
the existing substituents and their individual effects; whether the groups have cooperative or antagonistic directing effects.
Ortho position is the most reactive towards electrophile
due to the highest electron density ortho positions.
But this increased reactivity is countervailed by steric hindrance between substituent and
electrophile. A nucleophilic substitution is a substitution reaction which the nucleophile
displaces a good leaving
group, such as a halide on an aromatic ring. This
mechanism is called SNAr
( the two-step addition-elimination mechanism), where electron withdrawing substituents activate
the ring towards nucleophilic attack. Addition-elimination reactions usually
occur at sp2 or sp
hybridized carbon atoms, in contrast to SN1 and SN2
at sp3.
Chloro and bromobenzene reacts with the very
strong base sodium amide (NaNH2) to give good yields of aniline.
Other nucleophilic aromatic substitution mechanisms
include benzyne mechanism and free radical
(SRN1) mechanism. Common
reactions of substituent groups on benzene ring include:
- Conversion of halogens
into other various substituents
- Modifying activating substituents
- Oxidative degradation of
alkyl chain
- Reduction of
nitro or carbonyl substituents
- Reversibility of the aromatic sulfonation reaction
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
to light yellow liquid |
|
ASSAY
|
99.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
6
-8 C |
|
WATER
|
0.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
250kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1
(Packing group: III) |
| UN
NO. |
2021 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN C, Risk Phrases: 20/21/22/34,Safety Phrases: 2/28A |
|
GENERAL INFORMATION OF CHLORINATED PHENOLS |
|
2-MONOCHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 95-57-8
EINECS
NUMBER
: 202-433-2
OTHER
NAME(S):
o-chloro-Phenol; 1-Chloro-2-hydroxybenzene; 2-Chloro-1-hydroxybenzene;
2-Chlorophenol; 2-Hydroxychlorobenzene; Chloro-2 phenol; o-Chlorophenic acid;
o-Chlorphenol (German); P-Chlorfenol (Czech);
MAJOR USES:
Intermedaite
for higher to 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol pentachlorophenol.
Polymer intermediate for fire-retardant varnishes; cotton fabric treatment to
provide rot resistance;ingredient in coal processing; topical antiseptics ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 40 mg/kg
UN Number: 2021
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing: 240kgs
in drum
|
C6H4Cl(OH) (128.56)

| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
light amber liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
8 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
175 - 176 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.24 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
550 C |
| SOLUBILITY |
Slightly soluble
in water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
63
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
99.5% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
8
- 9 C
|
|
|
|
|
3-MONOCHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 108-43-0
EINECS
NUMBER
: 203-582-6
OTHER
NAME(S):
m-Chloro-phenol; 3-Chloro-1-hydroxybenzene; 3-Chlorophenol;
3-Hydroxychlorobenzene; m-Chlorophenic acid; m-Chlorophenol;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; topical antiseptics ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 570 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020 (Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: III)
Packing: 240kgs in
drum
|
C6H4Cl(OH) (128.56)
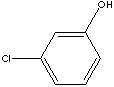
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
semi-solid |
| MELTING POINT |
33 - 35 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
214 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.26 - 1.27 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
97
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
33 - 35 C |
|
|
|
|
4-MONOCHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 106-48-9
EINECS
NUMBER
: 203-402-6
OTHER
NAME(S):
p-chloro-phenol; 4-Chlorophenol; 4-Chloro-1-hydroxybenzene;
4-Hydroxychlorobenzene; p-Chlorfenol (Czech); p-Chlorophenic acid;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
higher
chlorophenols; intermediate
dyes, fungicides, and drugs.topical antiseptics ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 670 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020 (Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: III)
Packing: 240kgs in
drum
|
C6H4Cl(OH) (128.56)
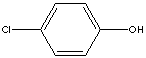
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
43 - 45 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
220 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.30 - 1.31 |
| SOLUBILITY |
soluble in ethanol,ether
benzene |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
115 C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
99.5% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
42
- 45 C
|
|
|
|
|
2,3-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 576-24-9
EINECS
NUMBER
: 209-399-8
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,3-Dichlorohydroxybenzene;
2,3-DCP; 2,3-Dichlorfenol;
1-Hydroxy-2,3-dichlorobenzene;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for agrochemicals and other
compounds; formulating fungicides, bactericides, algicides;
topical antiseptics; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral mouse LD50: 2376 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020 (Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: III)
Packing:
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
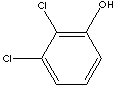
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to yellow
crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
56 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
214 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in
water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
115 C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
2,4-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 120-83-2
EINECS
NUMBER
: 204-429-6
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,4-Dichlorohydroxybenzene;
2,4-DCP; 2,4-Dichlorfenol;
4,6-Dichlorophenol;
1-Hydroxy-2,4-dichlorobenzene; NCl-C55345;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for production of 2,4-D and other related
herbicides; ingredient
of antiseptics; starting material higher chlorophenols;
Intermediate for production of Sesone,Nitrofen, Nemacide;
antihelminthic drug; polyester films; mothproofing; miticide;
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 47 mg/kg
UN Number: 2928
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing: 50kgs in
drum
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
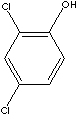
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to yellow
crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
41 - 44 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
209 - 210 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.382 |
| SOLUBILITY |
Slightly soluble
in water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
104
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
41 - 44 C |
|
|
|
|
2,5-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 583-78-8
EINECS
NUMBER
: 209-520-4
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,5-Dichlorohydroxybenzene;
2,5-DCP; 2,5-Dichlorfenol;
1-Hydroxy-2,5-dichlorobenzene;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; topical antiseptics;
antihelminthic drug; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 580 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020 (Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: III)
Packing: 50kgs in
drum
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
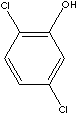
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to light brown crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
56 - 58 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
211 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
100 C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 87-65-0
EINECS
NUMBER
: 201-761-3
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,6-Dichlorohydroxybenzene;
2,6-DCP; 2,6-Dichlorfenol;
1-Hydroxy-2,6-dichlorobenzene;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; antihelminthic drugs;
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number:
Packing: 50kgs in
drum
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
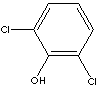
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to light brown crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
65 - 68 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
218 - 220 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
98.0%
min |
|
MELTING POINT |
64 - 67
C |
|
|
|
|
3,4-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 95-77-2
EINECS
NUMBER
: 202-450-5
OTHER
NAME(S):
4,5-Dichlorophenol;
3,4-Dichlorohydroxybenzene; 3,4-DCP; 3,4-Dichlorfenol;
1-Hydroxy-3,4-dichlorobenzene;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral mouse LD50: 1685 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing: 25kg
sin bag
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
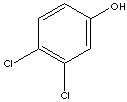
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to light brown crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
65 - 68 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
145 - 146 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Slightly soluble
in water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
65 - 68 C |
|
|
|
|
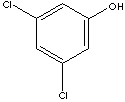
3,5-DICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 591-35-5
EINECS
NUMBER
: 209-714-9
OTHER
NAME(S):
3,5-Dichlorophenol;
3,5-Dichlorohydroxybenzene; 3,5-DCP; 3,5-Dichlorfenol;
1-Hydroxy-3,5-dichlorobenzene;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral mouse LD50: 2389 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing:
|
C6H3Cl2(OH) (163.00)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to light brown crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
67 - 69 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
233 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in
water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
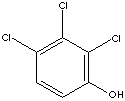
2,3,4-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 15950-66-0
EINECS
NUMBER
: 240-083-2
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-2,3,4-Trichlorobenzene;
2,3,4-TCP;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 2389 mg/kg
UN Number:
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to tan flakes |
| MELTING POINT |
79 - 81 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
248 - 250 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in
water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
62
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
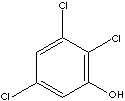
2,3,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 933-78-8
EINECS
NUMBER
: 213-272-2
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-2,3,5-Trichlorobenzene;
2,3,5-TCP; NCl-C61187;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to tan flakes |
| MELTING POINT |
57 - 59 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
248 - 250 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in
water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
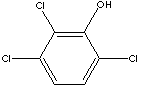
2,3,6-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 933-75-5
EINECS
NUMBER
: 213-271-7
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-2,3,6-Trichlorobenzene;
2,3,6-TCP; NCl-C02904;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
agrochemicals and other compounds; formulating
fungicides, bactericides, algicides; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number:
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to tan flakes |
| MELTING POINT |
55 - 58 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
253 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in
water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
78
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
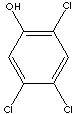
2,4,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 95-95-4
EINECS
NUMBER
: 202-467-8
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-2,4,5-Trichlorobenzene;
2,4,5-TCP; Collunosol;
Dowicide B;
Nurelle;
Preventol 1;
MAJOR USES:
Intermediate for
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) or
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxypropionic acid (2,4,5-TCPPA) and related herbicides; fungicide,
bactericide, algicide; ingredients of germicidal soaps; germicide for preservation for
plywood; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to tan flakes |
| MELTING POINT |
67 - 69 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
248 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
98.0%
min |
|
MELTING POINT |
67 - 69
C |
|
|
|
|
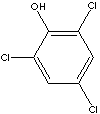
2,4,6-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 88-06-2
EINECS
NUMBER
: 201-795-9
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-2,4,6-trichlorobenzene;
2,4,6-TCP; Dowicide 2; Omal;
Phenachlor;
MAJOR USES:
Precursor for higher chlorophenols; intermediate in preparation of insecticides,
germicide for preservation of
wood, leather, glue, and textiles;; ingredients of germicidal soaps. ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 820 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1, Packing Group: III)
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to tan flakes |
| MELTING POINT |
65 - 66 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
246 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.49 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
70
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
65 - 68
C |
|
|
|
|
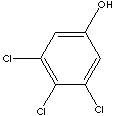
3,4,5-TRICHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 609-19-8
EINECS
NUMBER
:
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxy-3,4,5-trichlorobenzene;
3,4,5-TCP;
MAJOR USES: ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number:
Packing:
|
C6H2Cl3(OH) (197.45)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
|
| MELTING POINT |
101 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
271 - 275 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.49 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
101
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
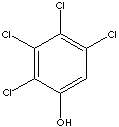
2,3,4,5-TETRACHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 4901-51-3
EINECS
NUMBER
: 225-531-7
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,3,4,5-tetrachlorhydroxybenzene;
2,3,4,5-tetrachlorophenate; Dowicide 7;
MAJOR USES:
Fungicide and bactericide for wood preservation; sapstain
(sodium salt form); pesticide; preservative for latex and leather,
plywood; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50:
UN Number:
Packing:
|
C6HCl4(OH) (231.89)
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
beige rystalline solid |
| MELTING POINT |
116-117 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
sublimes |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.67 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
2,3,4,6-TETRACHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 58-90-2
EINECS
NUMBER
: 200-402-8
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,3,4,6-tetrachlorhydroxybenzene;
2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenate; Dowicide 6;
MAJOR USES:
Fungicide and bactericide for wood preservation; sapstain
(sodium salt form); pesticide; preservative for latex and leather,
plywood; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 140 mg/kg
UN Number: 2811(Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: II)
Packing:
Cancer suspect agent
|
C6HCl4(OH) (231.89)
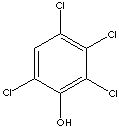
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
light brown crystalline solid |
| MELTING POINT |
62 - 64 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
150 at 16 mmHg |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.6 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
100
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
|
2,3,5,6-TETRACHLOROPHENOL
CAS
NUMBER : 935-95-5
EINECS
NUMBER
: 213-310-8
OTHER
NAME(S):
2,3,5,6-tetrachlorhydroxybenzene;
2,3,5,6-tetrachlorophenate;
MAJOR USES:
Fungicide and bactericide for wood preservation; sapstain
(sodium salt form); pesticide; preservative for latex and leather,
plywood; ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 140 mg/kg
UN Number: 2020
(Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: II)
Packing:
|
C6HCl4(OH) (231.89)
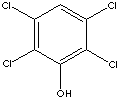
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
light brown crystalline solid |
| MELTING POINT |
115 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
288 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.84 |
| SOLUBILITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
100
C |
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
|
|
| PENTACHLOROPHENOL CAS
NUMBER : 87-86-5
EINECS
NUMBER
: 201-778-6
OTHER
NAME(S):
1-Hydroxypentachlorobenzene; 2,3,4,5,6-Pentachlorophenol; Dowicide 7; Durotox;
Pentachlorphenol (German); Pentaclorofenolo;
MAJOR USES:
preservative
for timber from fungal rot and wood-boring insects;
intermediate for pesticides and fungicides;
cooling towers additive of electric plants;
as additives to adhesives; additvie in shingles, brick walls, concrete blocks, insula
tion, pipe sealant compounds, photographic solutions, and textiles and in
drilling mud in the petroleum industry ADDITIONAL
INFORMATIO
Oral rat LD50: 27 mg/kg
UN Number: 3155
(Hazard Class: 6.1,
Packing Group: II)
Packing:
|
C6Cl5OH
(266.34)
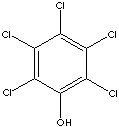
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
light brown crystalline solid |
| MELTING POINT |
190 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
310
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.979 |
| SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble
in water |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| PURITY |
86.0%
min |
|
ALKALI
INSOLUBLES |
0.5%
max |
|
MELTING POINT |
180
C
|
|
|
|


















