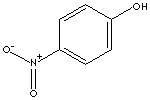
| p-NITROPHENOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 100-02-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-811-7 | |
| FORMULA | C6H5NO3 | |
| MOL WT. | 139.11 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2908.90 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 202 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 4-Hydroxynitrobenzene; Paranitrofenolo (Italian); | |
| 4-Nitrophenol; Niphen; PNP; mononitrophenol; 4-Notrophenol; 4-Nitrofenol (Dutch); | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow to brown crystals | |
| MELTING POINT |
113 - 114 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
Decomposes | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Slightly soluble (1.6 g/100ml) | |
| pH |
| |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 1.479 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 2 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
169 C | |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Mononitrophenols are used as intermediates for the synthesis of a number of organophosphorus pesticides, azo dyes, and some medical products as well as their corresponding amonophenols by reduction. some end products derived from mononitrophenols include dyes and pigments, acetaminophen (from p-aminophenol), carbofuran, phosalon (insecticides form o-nitrophenol), parathion,parathion-methyl, fluorodifen (insecticides form p-nitrophenol), nitrofen, bifenox (herbicides form p-nitrophenol), fungicides, and rubber chemicals. Nitrophenol is used as a pH range indicator (colorless at 5 and yellow at 7). Nitrophenol derivatives are used as intermediates for the synthesis of a number of target products. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to brown crystals | |
| TOTAL AMINO |
92.0% min | |
| MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 1663 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/21/22-38, Sety Phrases: 28 | ||