|
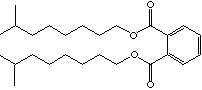
DIISONONYL PHTHALATE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. |
28553-12-0 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 271-090-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C6H4(COOC9H19)2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 418.61 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2917.33.0050 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | DINP; Isononyl alcohol phthalate; DINP; Palatinol DN; Palatinol N; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid diisononyl ester; Bis(7-methyloctyl) phthalate; Di(C8-C10) branched alkyl phthalate; Di(isononyl) phthalate branched; Di(C8-10, C9 rich) branched alkyl phthalates; Vestinol 9; Vestinol NN; Vinylcizer 90; Witamol 150; Other RN: 68515-48-0; 105009-97-0; 41375-91-1; 58033-90-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | c1(c(C(OCC[C@@H](CC(C)(C)C)C)=O)cccc1)C(OCC[C@@H](CC (C)(C)C)C)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Dielectric (electric insulating) fluid, Plasticizer, Polymer Additive |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear viscous liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 279 - 287 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.972 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble(0.2 mg/l at 20 C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| log Pow | 9.37 (Octanol-water) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HENRY'S LAW | 1.49E-06 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OH RATE | 2.34E-11 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
405 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | 93 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Phthalates are by far the most widely used plasticisers, primarily to make soft
and flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for the applications in the industry of
automotive, building & construction material, cable, flooring, medical
device and toys. Phthalates make the long polyvinyl molecules to slide against
one another. Minor quantity of phthalates are used in adhesives, caulk,
sealants, paint to improve work performance. Small molecule phthalates are used
as solvents in perfumes to provide longer linger longer and in nail polish to
prevent chipping. They are also used as ingredients of insect repellents, as
solvents in lacquer and pesticides, and as dye carrier. They are used as textile
lubricating agents and as solid rocket propellents. Phthalates are produced by
the reaction of phthalic anhydride with appropriate alcohols from methanol up to
isodecanol (C13), either as a straight chain or with some branched in the
presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a catalyst. Excess alcohols are
recovered and recycled and phthalates are purified by vacuum distillation and/or
activated charcoal. A wide range of phthalates of varying chain length and
structure provides each adequate properties and cost-effective for various
processing and mechanical requirements. C8 - C9 phthalates, such as di-2-ethyl
hexyl phthalate (DEHP or called DOP), diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) and diisononyl
phthalate (DINP) are the most widely used general purpose phthalates. DOP is the
dominant plasticizer used in PVC, providing low cost. Short chain phthalates (C3
- C7) are used when rapid setting and stain resistance is required. 2-Ethyl
hexanol, produced by the dimerisation of butyraldehyde obtained from propylene,
is cheaper than isononyl alcohol which are prepared by the carbonylation of an
olefin. Long chain phthalates (C11 - C13) are used when high temperature
stability is required. C1 and C2 phthalates are used as solvents. Special
phthalates which contain aromatic ring in the side chain are used when
fast-fused is required. Diallyl phthalate is used as a crosslinking agent,
plasticizer or dying carrier for polyesters.
DINP is a general ,next to DOP,plasticizer. Heat resistance, low temperature resistance and volatility resistace are properties are usd to PVC. http://www.chemcas.com/ Search http://www.cpsc.gov/ www.regulations.gov/ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ESTER CONTENT |
99.6% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.972 ± 0.002 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COLOR, APHA | 25 max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.484 ± 0.003 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WATER | 0.05% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING |
195 kg in drum |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not regulated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 62-63, Safety Phrases: 23-36/37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||