DIOCTYL ADIPATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
103-23-1
TOXICITY
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)adipate; Adipic acid di(2-ethylhexyl) ester;
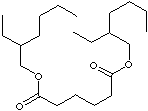
C([C@@H](CCCC)CC)OC(CCCCC(OC[C@@H](CCCC)CC)=O)=O
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear liquid
417 C
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
Soluble in aceton, ether, ethanol
245 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.449 ~ 1.448
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Dioctyl adipate
PubChem Compound Summary - Dioctyl adipate
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Dioctyl adipate
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Dioctyl adipate
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Dioctyl adipate
http://www.chem.unep.ch/SIDS Initial Assessment Report
http://www.sustainableproduction.org/
Chemical
Alternatives to Phthalates:A number of substances have been identified
as alternative plasticizers. These alternatives include citrates,
sebacates, adipates, and phosphates. They are being substituted
in products that traditionally use phthalates, such as toys, childcare
articles and medical devices. In addition to their application as
alternative PVC plasticizers, these substances are also being used
as solvents and fixatives in cosmetic products, inks, adhesives,
and other consumer products. Most of these alternative plasticizers
are not well studied with regard to their potential effects on human
health and the environment. Although many of these alternatives
show promising application potential, significant exposure may lead
to adverse health effects. Like phthalates, these alternative plasticizers
are not chemically bound to the polymer and can leach out of products.
Some documented effects from exposure to the alternative plasticizers
that are currently being used in children��s products and other
consumer products include eye, skin, and respiratory irritations.
There is also evidence of effects on the kidney, liver, spleen,
testes, and uterus. Most evidence on human health effects is derived
from laboratory studies as few epidemiologic studies have been conducted
on these materials. In addition, some alternative plasticizers may
be toxic to aquatic organisms and may not biodegrade in the environment.
Table 2 identifies some alternative plasticizers currently used
in children��s and other consumer products, and their potential
health and environmental effects.
Local:
There are almost infinite esters obtained from thousands of potential starting
materials. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol,
e.g., carboxylic acid esters, phosphoric acid esters, and sulfonic acid esters.
Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications.
Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent
carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds
are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants,
detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile
treatments and emollients, They are also used
as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost
infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor
pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the
proper application selections.
Adipic Acid Esters are used as low-temperature-resistant and low-viscosity plasticizer for PVC and its copolymers and cellulose esters e.g. cellulose acetate butyrates and cellulose propionates. They are used as solvent carriers or coupling agents for polyurethane and photographic films. Lower chain esters of adipic acid are used as high-boiling, biodegradable, low-toxicity solvents and antiperspirants. Longer chain esters are used as lubricants offering stable lubricity, corrosion protection, biodegradability, and performance properties at both high and low temperatures. They are used as intermediates to produce other chemical compounds.
DOA (dioctyl adipate) is a light colored, oily liquid generally used as a plasticizer for PVC and is sometimes blended with other plasticizers such as DOP and DOTP. DOA features flexibility at low temperatures, good electrical properties, good resistance to weathering, and good stability to heat. DOA is used to produce clear films for food packaging applications. In addition, it is compatible with nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose, most synthetic rubbers, and high-butyryl cellulose acetate butyrates. stability to heat. DOA is used to produce clear films for food packaging applications. Adipic Acid Esters (C5 - C10) are used as low-temperature-resistant and low-viscosity plasticiser for polymers and cellulose esters. Short chain esters are used as high-boiling, biodegradable, low-toxicity solvents and antiperspirants. Long chain esters of adipic acid are used as lubricants for the functions of stability, superior lubricity, corrosion protection, biodegradability, and excellent performance at both high and low temperatures. They are used as intermediates to produce other chemical compounds.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ADIPIC ACID: Adipic Acid (also called hexanedioic acid) is a white, crystalline compound of C6 straight-chain dicarboxylic acid; slightly soluble in water and soluble in alcohol and acetone. Almost all of the commercial adipic acid is produced from cyclohexane through two sequent oxidation processes. The first oxidation is the reacting of cyclohexane with oxygen in the presents of cobalt or manganese catalysts at a temperature of 150 - 160 C, which produce cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Then, the intermediates are further reacted with nitric acid and air with a catalyst (copper or vanadium) or without nitric acid. Cyclohexane can be prepared by the hydrogenation of benzene. There are other ways such as the reactions using phenol, butadiene, and various fats as the starting material. Adipic acid consumption is linked almost 90% to nylon production by the polycondensation with hexamethylenediamine. Nylon, having a protein-like structure, is further processed into fibers for applications in carpeting, automobile tire cord and clothing. Adipic acid is used in manufacturing plasticizers and lubricants components. It is used in making polyester polyols for polyurethane systems. Food grade adipic acid is used as gelling aid, acidulant, leavening and buffering agent. Adipic acid has two carboxylic acid, -COOH, groups, which can yield two kinds of salts. Its derivatives, acyl halides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles, are used in making target products such as flavoring agents, internal plasticizers, pesticides, dyes, textile treatment agents, fungicides, and pharmaceuticals through further reactions of substitution, catalytic reduction, metal hydride reduction, diborane reduction, keto formation with organometallic reagents, electrophile bonding at oxygen, and condensation.
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
ESTER CONTENT
99.5% min
0.927 ± 0.003
1.446 ± 0.003 at 20 C
HEAT LOSS
0.1% max
5.0 x 1011 at ��-cm at 30 C
200kgs in drum, bulk
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May cause skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritation. The toxicological properties have not been fully investigated. Target Organs: Liver, Kidney
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS
HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319
P STATEMENTS
P305+P351+P338
XI
RISK PHRASES
36/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36
PRICE INFORMATION