| N-METHYLAMINOETHANOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 109-83-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-710-0 | |
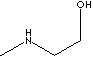
| FORMULA | CH3NHCH2CH2OH | |
| MOL WT. | 75.11 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2922.19 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral, rat LD50: 1390 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | N-Methyl-2-ethanolamine; N-Methylethanolamine; | |
| methyl ethanolamine; beta-(methylamino)ethanol; monomethylaminoethanol; methyl(beta-hydroxyethyl)amine; monoethylethanolamine; Methylaminoethanol; Hydroxyethylmethyleneimine; N-Methyl-2-aminoethanol; 2-Methylaminoethanol; | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | colorless to slight yellow viscous liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT |
155 -156 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.94 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Miscible | |
| pH | Strong base | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 2.59 | |
| AUTOIGNITION | 349 C | |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
90 C | |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Alkanolamines have the combined physical and chemical characteristics of both alcohols and amines in one molecule, which makes them useful intermediates in the synthesis of various target molecules for the use in many diverse areas such as pharmaceutical, urethane catalysts, coatings, personal care, products, Water treatments, corrosion inhibitors, and gas treating industries. There are 1°, 2º or 3º nitrogen atom and one hydroxyl group at least in alkanolamines. Alkanolamines react with inorganic acids carboxylic acids to form salts, soaps, esters, or amides. Alkanolamines are used in both water- based and solvent-based coatings to enhance the solubility, reducibility, pigment dispersing and pH stability. They are used in cathodic electrodeposition systems and as a catalyst for chain-extend. Alkanolamines are used to prepare surface-active soaps through reaction with fatty acids. Surface-active soaps are used commercially as a emulsifier, lubricants, detergents, pesticides and personal care products. Alkanolamines maintain a constant alkalinity in the boiling water flows and condensate not to form solid products which would impede line flow. This function is applied for corrosion Inhibits. Alkanolamines are widely employed in the preparation of water soluble cationic flocculants and ion exchange resins which adsorb solid and colloidal particles by electrostatic attraction. They are used for water treatment industry. Alkanolamines and their derivatives are widely used as intermediates for the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients such as procaine, antihistamines analgesics from N,N-dimethylethanolamine or N-methyldiethanolamine. Alkanolamines are used to remove Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and CO2 gas from gas streams in natural and refinery gas operations. N-Methylethanolamine, being a secondary amine, has the highest freezing point of this family at -5 C among alkanolamines. It reacts with fatty acids in an equimolar ratio to produce amides and amide esters. N-methylethanolamine is used to as a catalyst for chain-extend to give high mole weight polyepoxides with a polyol. It is used as an intermediate for textile auxiliaries, coatings, pharmaceuticals (particularly antihistamines such as diphenhydramine), optical brighteners, agrochemicals. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
colorless liquid, free of suspended matter | |
| ASSAY (G.C) |
99.0% min | |
|
WATER (K.F) |
0.5% max | |
|
COLOR (APHA) |
15 max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 185kgs in Drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 1719 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 21-34 Safety Phrases: 23-26-36-45 | ||