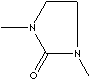
| N,N'-DIMETHYLETHYLENEUREA | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO | 80-73-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-304-8 | |
| FORMULA | C5H10N2O | |
| MOL WT. | 114.15 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2924.21.5000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Rat LD50 oral: 1.19ml/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidone; DMEU; DMI; Dimethyl imidazolidinone; | |
| 1,3-Dimethylimidazolidin-2-one; 1,3-Dimetilimidazolidin-2-ona; Karbomos TsEM; N,N'-Dimethylimidazolidinone; Rhonite 1; | ||
|
SMILES |
C1(N(CCN1C)C)=O |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Amide solvent |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | 8 - 9 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 224 - 226 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.05 - 1.06 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| pKa | (Dissociation Constant at 20 C) | |
| log Pow | -0.31 (Octanol-water) | |
| VAPOR PRESSURE | (mmHg at 25 C) | |
| HENRY'S LAW | (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |
| OH RATE | 9.14E-12 (Atmospheric at 25 C ) | |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.468 - 1.473 | |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS | ||
| Solvent is a substance, usually a liquid, that acts as a dissolving agent or that is capable of dissolving another substance. In solutions of solids or gases in a liquid, the liquid is the solvent. In all other homogeneous mixtures (i.e., liquids, solids, or gases dissolved in liquids; solids in solids; and gases in gases.), solvent is the component of the greatest amount. The minor proportion substances are called solutes. The solvent offers several functions during a chemical reaction. It solves the substance that reacts with another one to produce a new set of substances (reactant) and the compound that supplies the molecule, ion, or free radical which is considered as the attacking species in a chemical reaction (reagent). The solvent is conductive to collisions between the reactants and reagents to transform the reactants to new products. The solvent also takes roll of temperature control, either to provide the energy of the colliding particles for speedy reaction and to absorb heat in exothermic reaction. The appropriate solvent should be selected based on the inactivity in the reaction conditions, dissolving the reagents as well as reactants, appropriate boiling point and easy removal at the end of the reaction. he most common solvent is water. Other common solvents which dissolve substances that are insoluble (or nearly insoluble) in water are acetone, alcohol, formic acid, acetic acid, formamide. BTX, carbon disulfide, diemthyl sulfoxide, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, ether, tetrahydrofuran, furfural, hexane and turpentine. They may be classified as polar and nonpolar types. They may be classified as polar and nonpolar types. Polar solvents, like water, have molecules whose electric charges are unequally distributed, leaving one end of each molecule more positive than the other. Usually polar solvent has O-H bond of which water (HOH), methanol (CH3OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are examples. Propanol, butanol, formic acid, formamide are polar solvents. Dipolar solvents which contain a C-O solid bond without O-H bond are acetone [(CH3)2C=O], ethyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH3), methyl ethyl ketone, acetonitrile, N,N-dimethylformamide and diemthyl sulfoxide. Nonpolar solvents, like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), benzene (C6H6), and diethyl ether ( CH3CH2OCH2CH3), have molecules whose electric charges are equally distributed and are not miscible with water. Hexane, tetrahydrofuran and methylene chloride are nonpolar solvents. 1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone is an aprotic, dipolar solvent containing two nitrogens in five-membered ring structure. It can replace for the other nitrogen containing solvents like hexamethylphosphoramide which is carcinogenic. It has high boiling and flash points, 225 C and 120 C respectively It features excellent solubility of organic and inorganic compounds as well as stability in hydrosilanediyl-transition metal complexes. It is used in various inorganic and organic compound synthesis including in the field of polymers, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and electronic parts. It is a suitable replacement for the carcinogenic solvent Hexamethylphosphoramide | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear liquid | |
|
PURITY |
98.0% min | |
|
COLOR, APHA |
50 max | |
|
WATER |
0.1% max | |
| BOILING POINT |
224 - 226 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1(Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2811 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 21/22-38-41, Safety Phrases: 26-36 | ||