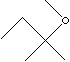
| tert-AMYL
METHYL ETHER
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 994-05-8 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 213-611-4 | |
| FORMULA | C2H5C(CH3)2OCH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 102.18 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 1602 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | TAME; tert-Pentyl methyl ether; 2-methoxy-2-methyl-Butane; | |
| 2-Methyl-2-methoxybutane; Methyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl ether; Methyl tert-amyl ether; Methyl 2-methyl-2-butyl ether; tertiary-amyl methyl ether; 1,1-Dimethylpropyl methyl ether; | ||
|
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear, colourless and flammable liquid with low viscosity. | |
| MELTING POINT | -80 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 85 - 87 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.764 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 12 g/l | |
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | 3.52 | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.3896 | |
| FLASH POINT |
-11 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| TAME (tert-Amyl Methyl Ether) is a volatile, low viscosity clear liquid at room
temperature with an ether odour; boiling point 86 C; melting point -80 C. TAME
is flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. It is slightly soluble in
water and very soluble ethers and alcohol and in most organic solvents including
hydro carbons. TAME is an ether which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two
carbon atoms. In tert-Amyl Methyl Ether, one carbon atom is that of a methyl
group and the other is the central atom in a tertiary amyl group. TAME may be prepared by reacting isoamylenes in a mixed C5 stream with methanol
in the presence of an acidic catalyst. The most
quantity produced worldwide is used as an oxygenate to gasoline. It is added
both to increase octane enhancement to replace banned tetraethyl lead and to
raise the oxygen content in gasoline. It is known that TAME in fuel reduces
exhaust emissions of VOC (volatile organic compounds: acetaldehyde, benzene,
1,3-butadiene, ethylbenzene, formaldehyde, toluene, xylenes, and particulate
organic matter) except formaldehyde. Ozone is formed by the reaction of sunlight
with NOx and VOCs. With strong solvating capabilities for a wide variety of
compounds, TAME is used as a reaction medium and extraction solvent to replace
methylene chloride, aromatics, and other ethers. TAME is a non-chlorinated
process solvent. It is used as a solvent for chromotographic techniques. The
sterically hindered tertiary butyl group imparts stability. It has also an acid
stability compare to other diether acetals. It is used as a paraffin-removing
agent alone or in combination with other solvents. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
C7 ETHERS |
1.0% max |
|
| AMYL ALCOHOL |
0.6% max |
|
|
WATERR |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | 1993 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| European Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: 11, Safety Phrases: 16 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ETHER |
||
| Ether
is any of a number of organic compounds characterized
by an oxygen atom joined by two carbon atoms that are
part of hydrocarbon groups. The general formula is ROR',
where R and R' are alkyl groups. Ethers are formed by
the condensation of two alcohols. They are similar to
alcohols but are generally less dense, less soluble
in water, and have lower boiling points. They are relatively
unreactive chemically. This unreative property makes
ethers valuable as solvents. Common names of ethers
simply list the alkyl groups in alphabetical order (ethyl
methyl ether, IUPAC name is methoxyethane). Epoxides
and crown ether are a special class of cyclic ethers.
Epoxide (oxirane) is a three-membered cyclic ether in
which an oxygen atom is joined to each of two carbon
atoms that are already bonded to each other. Crown Ether
is a macrocyclic polyether whose structure contains
hydrogen, carbon and oxygen atoms. Each oxygen atoms
are confined between two carbon atoms and exhibits a
conformation with a hole (accordingly called "crown").
|
||