PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
21871-47-6
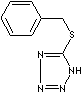
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Oligonucleotide is a short DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) sequence, typically made up of a few (2–20) covalently linked nucleotides. In molecular genetics, a short sequence synthesized to match a region where a mutation is known to occur, and then used as a probe for detecting complementary DNA or RNA. Oligonucleotides are currently used for genomic,proteomic and drug discovery technologies. Tetrazole is the traditional oligonucleotide synthesis activato for good coupling efficiency and to decrease the coupling times. But there are disadvantages of tetrazole; crystallisation problem from solution and potential explosive property at room temperature. Some alternatives have been recommended;
- 5-Ethylthio-1H-tetrazole [CAS RN: 89797-68-2]
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% min
LOSS ON DRYING
0.3% max
MELTING POINT