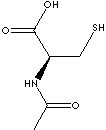
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Acetylcysteine is the N-acetyl derivative of L-cysteine, an amino acid having a thiol group. L-Cysteine oxidizes to cystine, which is the dimeric form of cysteine joined by a disulfide bond. The disulfide bond is easily reduced to the corresponding thiol (-SH). N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is metabolized into glutathione (γ-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine), a tripeptide existing in both the reduced thiol form and the oxidized disulfide form. It involves in various redox reactions such as the formation of disulfide bonds in proteinsthe and destruction of peroxides and free radicals. This function confers antioxidant effects preventing oxidative damage by reduction of methemoglobin and peroxides. Acetylcysteine is used as a dietary supplement that is metabolized into the antioxidant glutathione. It has also been shown to have antiviral effects in patients with HIV due to inhibition of viral stimulation by reactive oxygen intermediates. Acetylcysteine is used as a mucolytic agent which is capable of reducing the viscosity of mucus for its removal. The viscosity of mucous is dependent upon the presence of disulfide bonds between these macromolecules and DNA. Acetylcysteine isolates the sulfide bonds.
Members of mucolytic agent
|
Agent |
CAS RN |
| Bromhexine hydrochloride | 611-75-6 |
| Acetylcysteine | 616-91-1 |
| Carbocysteine | 2387-59-9 |
| Bromhexine | 3572-43-8 |
| Ambroxol | 18683-91-5 |
| Ambroxol hydrochloride | 23828-92-4 |
| 4-Amino-3-bromo-5-((diethylamino)methyl)benzoic acid ethyl ester HCl | 57814-29-6 |
| Domiodol | 61869-07-6 |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0 - 102.0%
SPECIFIC ROTATION
1.0% max
pH
2.0 - 3.0
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
0.5% max
Peptide is the members of the compounds composed of two or more amino acids joined by the linking between one amino acid residue and the carboxyl group of the next amino acid by hydrolysis into linear, branched or cyclical structures. The link is an amide bond, and is sometimes referred to as a peptide bond. Peptides are playing a promising role in the molecular biology and in the creating medicines. Peptides are used in the study of protein structure and function, antibodies for the inhibition of cancer, for the study of protein structure and function research. Peptides are also used as instrumental in mass spectrometry. Biological activities of peptide are applicable in the fields of nutrition, medicine, and cosmetics.
- Dipeptide: a molecule consisting of two amino acids
- Tripeptide a molecule consisting of three amino acids
- Octapeptide: a molecule consisting of eight amino acids
- Oligopeptide: a polypeptide composed of approximately 2-12 amino acids length (or 3 to 40 component amino acids)
- Polypeptide: a single molecule composed of approximately 13 or more amino acids.
- Protein: a linear polypeptides that are normally synthesized on ribosomes.