PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
207-549-7
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
SMILES
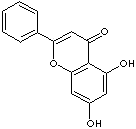
c12c(oc(c3ccccc3)cc1=O)cc(O)cc2O
CLASSIFICATION
Flavone
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Soluble in alkali hydroxide solution, slightly soluble in alcohol, chloroform, ether.
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Chrysin
Google Scholar Search - Chrysin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Chrysin
PubChem Compound Summary - Chrysin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Chrysin
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Chrysin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Chrysin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Chrysin
Local
Chrysin is a bioflavone, considered to have bioactive effect on human health as antioxidant, radical scavenger, antiinflammatory, carbohydrate metabolism promoter, immunity system modulater. Chrysin is a antimetabolite against benzo[a]pyrene.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% min
WATER
0.5% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FLAVONOID
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin.
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. May cause eye irritation. May be harmful if swallowed.
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
22-24/25