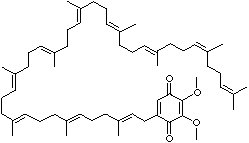
| Udekinon;
(all-E)-2-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-
tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione;
2-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Decamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecae
nyl)-5,6-
dimethoxy-3-methyl-p-benzoquinone;
2-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39-Dec amethyl- 2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-
dimethoxy- 3-methyl-p- benz oquinone;
Ubiquinone 50; CoQ10 ; Emitolon; Heartcin; Inokiten; Justquinon;
Luvacor; Neuquinon; Neuquinone; Ubidecarenona; Ubidecarenone; Ubiquinone Q10; |
|
Coenzyme Q is a fat soluble quinone terminated compound with a sequence of
conjugated isoprene units. The structure is related to carotenoid, vitamin K and
vitamin E. It is stable in acid but insoluble in a;kali. The most common
coenzyme Q in human mitochondria is coenzyme Q 10 (ubidecarenone) which contains
ten isoprene units. The chemical designation is
2-((2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E,34E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39- decamethyl-
2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34,38-tetracontadecaenyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-
2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione.
It occurs in the lipid core of inner mitochondrion membranes. It is an essential
component of the electron transfer chain to ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase.
Redox (Oxidation-reduction) reactions occur simultaneously and represent the
main source of biological energy. Coenzyme acts as a reduction/oxidation agent
or as a similar electron transfer. It acts as an endogenous antioxidant to
prevent mitochondrion membranes and DNA. It is called ubiquinone or ubiquinol as
it is is readily oxidized to alcohol. Because of its antioxidant property,
Coenzyme Q is used as a dietary supplement. Coenzyme antioxidant benefits to the brain is also studied for the
treatment of neurodegenerative disease.
Coenzyme is a nonprotein organic
molecule that that binds with the inactive apoenzyme to form holoenzyme (the
active enzyme). Coenzymes frequently contain phosphorylated water-soluble
vitamins as part of their structure. Non-vitamin coenzymes include heme
coenzymes in catalytic hemoproteins. The prosthetic group (nonprotein portion of
the enzyme) functions as an acceptor of electrons or functional groupings. The
apoenzyme can function singly. Certain enzymes need metal (copper, manganese,
and magnesium) ions for the activation. Groups of coenzyme include:
- Adenosine triphosphate
- Biopterin
- Biotin
- Cobalamins
- Coenzyme PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
- Flavins
- Glutathione
- Heme
- Lipoic acids
- NAD
(Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
- NADP
(Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate)
- Nicotinamide nucleotides
- Pyridoxal
Phosphate
- Sphingolipid
Activator Proteins
- Tetrahydrofolates
- Thiamine
Pyrophosphate
- Ubiquinones
|