FISETIN
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Fisetin; Fietin; Viset; C.I. Natural Brown 1; C.I. 75620;
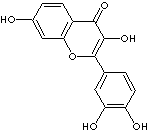
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; 3,3',4',7-Tetrahydroxyflavone; 5-Desoxyquercetin; Cotinin; Fustel; Fustet; 5-Desoxyquercetin; 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,7- dihydroxy-chromen-4-one;
SMILES
c1(c2cc(c(O)cc2)O)oc2c(ccc(c2)O)c(c1O)=O
CLASSIFICATION
Flavonol, Topoisomerase inhibitor, Catechol
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
yellow to brown crystalline powder
330 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Fisetin
Google Scholar Search - Fisetin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Fisetin
PubChem Compound Summary - Fisetin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Fisetin
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) - Fisetin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Fisetin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Fisetin
Local
A brown pigment found in woody plants. An analogue of quercetin. coloring principle of young fustic. Fustin (CAS RN: 20725-03-5) is the 2,3-Dihydrofisetin. Myricetin (3,3',4',5,5',7-Hexahydroxyflavone), Morin (2',3,4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone), Fisetin (3,3',4',7-Tetrahydroxyflavone are naturally-occurring flavonoids. They have antioxidant properties which protect cells against oxygen radical damage. They are also reported inhibit xanthine oxidase, a free-radical generating enzyme and show and inhibit the oxidation of LDL (low density lipoprotein) by free radicals.
APPEARANCE
yellow to brown crystalline powder
IDENTIFICATION
passes Test IR
ASSAY
98% min (HPLC)
ASH
0.5% max
LOSS ON DRYING
3.0% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FLAVONOID
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone):Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin
PRICE INFORMATION