|
Amino Acid is
any of the organic compounds in which one (or more ) amino group
(-NH2) and one (or more )
carboxylic acid group (-COOH) are both present with general formula
R-CH(NH2)COOH containing
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and in certain cases sulfur atoms. Two
groups attached to the same carbon (called the alpha-carbon atom at the end of
the compound) are polymerized to form peptides and proteins. The amine group is
protonated to form -NH3+ at low pH. The
carboxylic acid group is deprotonated to form -CO2- at high pH. The
carbon atom in the carboxyl group of one amino acid binds covalently to the
nitrogen atom in the amino group of another amino acid to form a peptide bond
with the release of a water molecule. Proteins are synthesized through the
covalent chemical polypeptide bonds. The sequence of these amino acids in the
protein polypeptides determines the shape, properties, and hence biological role
of the protein that function as chemical messengers and as intermediates in
metabolism. Proteins are composed of various proportions of about 20 commonly
occurring amino acids. Plants or other biological systems can synthesize amino
acids from simple inorganic compounds, but animals rely on adequate supplies in
their diet. More than 100 common amino acids occur in plants or in other
microorganic systems. The 20 amino acids commonly found in animals are Alanine,
Arginine, Asparagine, Aspartic Acid, Cysteine, Glutamic Acid, Glutamine,
Glycine, Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine,
Proline, Serine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine, and Valine. Many of the amino
acids can be synthesized in the human or animal body from other cellular
metabolites when needed (called Non-essential Amino Acids). Animals are not able
to synthesize some amino acids necessary in metabolism in sufficient quantities.
It must therefore be present in the diet (called Essential Amino Acids). In man,
these essential amino acids are Arginine, Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine,
Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan and Valine. Tryptophan
is formed from proteins during digestion by the action of proteolytic enzymes
and is necessary for normal growth and development. Branched amino-acids
(Valine, Isoleucine and Leucine ) with tryptophan and phenylalanine (aromatic
side chain amino acids) contribute to the structure of protein by the tendency
of its side chain composed only of carbon and hydrogen to participate in
hydrophobic interactions which determines the tertiary structure of the peptide
chain. Infants require greater amounts of tryptophan than adults. Only the
l-stereoisomer is biologically active form in mammalian protein. Tryptophan is
also a precursor for serotonin (a neurotransmitter), melatonin (a neurohormone)
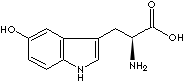
and niacin (a vitamin of the B complex). L-5-hydroxytryptophan
is a precursors of catecholamines
and serotonin. Serotonin, also called 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HTP), is an indole-containing
amino acid. In higher animals, it is found in high concentrations in many
tissues including in gastric mucous membranes, pineal body, central nervous
system and brain. Low levels are found in urine in the form of breakdown
products, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). It is also found in bacteria and
in many plants. Serotonin is produced from tryptophan by hydroxylation and
decarboxylation. It is a monoamine vasoconstrictor, plays a role in brain and
nerve function and in stimulation of the smooth muscles, regulation of cyclic
body processes and pharmacologic actions. |