PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
128446-36-6
1310
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Decomposes (180 - 182 C)
> 200g in100 ml
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Some examples of commercially available cyclodextrin, or derivatives thereof, are as follows:
- alpha-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 10016-20-3)
- alpha-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-60-1)
- alpha-Cyclodextrin, sulfated Sodium salt Hydrate (CAS #: 699020-02-5)
- Hexakis (2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Hexakis (2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Hexakis(2,3,6-tri-O-octyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 140395-31-9)
- Hexakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 53784-82-0)
- Hexakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 131105-41-4)
- Hexakis (6-O-tertbutyl-dimethylsilyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Butyl-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-alpha-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-33-3)
- beta-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 7585-39-9)
- beta-Cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 68168-23-0)
- beta-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-61-2)
- beta-Cyclodextrin sulfate
- beta-Cyclodextrin, sulfated Sodium salt (CAS #: 37191-69-8)
- Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 94035-02-6)
- 6-Monodeoxy-6-monoamino-beta-cyclodextrin
- 6-O-alpha-D-Glucosyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 92517-02-7)
- 6-O-alpha-Maltosyl-beta-cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 104723-60-6)
- Heptakis-6-azido-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis(2,3-di-O-acetyl-6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 196398-66-0)
- Heptakis-(2,3-di-O-methyl-6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 201346-23-8)
- Heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 51166-71-3)
- Heptakis-(2,6-di-O-ethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 111689-03-3)
- Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 55216-11-0)
- Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis-(2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 23666-43-5)
- Heptakis-(2,3,6-tri-O-ethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 111689-01-1)
- Heptakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 30754-23-5)
- Heptakis-6-(dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl)-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Monoacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Diacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Triacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 23739-88-0)
- Heptakis(3-O-acetyl-2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 131889-29-7)
- Heptakis-(6-O-maltosyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis(6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 197587-31-8)
- Heptakis(6-O-t-butyldimethylsilyl-2,3-di-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-(2-hydroxypropyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2,6-Di-O-)ethyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2-Carboxyethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxyethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-32-2)
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-35-5)
- Butyl-beta-cyclodextrin
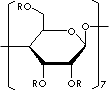
- Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-36-6)
- Silyl((6-O-tert-butyldimethyl)-2,3,-di-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- gamma-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 17465-86-0)
- gamma-Cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 91464-90-3)
- gamma-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-62-3)
- Sulfopropyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Carboxymethyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,6-di-O-pentyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis-6-(dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl)-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 53784-84-2)
- Octakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 168296-33-1)
- Octakis (6-O-t-butyldimethylsilyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-34-4)
- Acetyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Butyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
PURITY
97.0% min
CLARITY
Clear and colorless in aqueous solution
SPECIFIC ROTATION
REDUCED COMPOUNDS
0.5% max
FREE CYCLODEXTRIN
0.1% max
SOLVENT RESIDUE
10 ppm max ( Methanol, methyl chloride)
ACIDITY
1.5% max
CHLORIDE
0.5% max
SULFATES
0.1% max
LOSS ON DRYING
5.0% max
Yeast and Mold: 100 /g max.
Salmonella: Negative / 25 g
Coliform: Negative /g
HEAVY METALS
5ppm max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF DEXTRIN