|
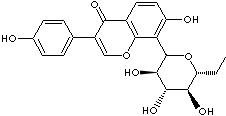
PUERARIN |
| Daidzein-8-C-glucoside; 7,4'-Dihydroxy-8-C-glucosylisoflavone; 8-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
3681-99-0 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C21H20O9 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
416.38 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Isoflavone |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Adrenergic beta-antagonist; Vasodilator agents; |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white power |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBILITIES |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
LD50 Intravenous mouse: 738mg/kg |
|
|
|
POTENTIAL HEALTH EFFECTS |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
|
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
| TARGET ORGANS |
Nerves., Heart, Blood |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
22-24/25 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Puerarin Puerarin (1) is a major effective ingredient extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Ge-gen (Radix Puerariae, RP). Recently, puerarin has been used to treat patients with coronary artery diseases (CAD). However, the mechanisms of puerarin on CAD are still not very clear. In this study, we investigated the role of puerarin on serum nitric oxide (NO) concentration, myocardial endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene expression, the protein expression of eNOS and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), as well as the level of protein kinase B (Akt/PKB) phosphorylation in rats with myocardial infarction. We found that puerarin (120 mg/kg/day, i.p.) could increase serum nitrite concentration in rat with myocardial ischemia (MI). It also induced the gene expression or activation of eNOS, protein expression of eNOS, and the Akt/PKB phosphorylation. From these results, we suggested that puerarin could increase serum nitric oxide level of rat with myocardial infarction, which should be one of the mechanisms of the therapeutic effect of puerarin on CAD. The increased expression of eNOS and the Akt/PKB pathway may be the underlying mechanism by which puerarin stimulates NO production. (http://cat.inist.fr/) Puerarin is an extract of natural Chinese medicine and has been extensively used in the treatment of coronary disease, hypertension, diabetes, etc. It has also been reported that puerarin can decrease oxidative damage and inhibit cell apoptosis. On the basis of our previous works that lens was oxidized by ONOO- and antagonized by puerarin, the present study was aimed to examine the feasibility of inhibiting cataract formation by puerarin, a chemical known to effectively scavenge ROS and inhibit protein glycation, both involved in the genesis of diabetic cataracts. We used flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry and gene array techniques to explore if puerarin decreases....... (http://www.actaps.com.cn/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white power |
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min (HPLC) |
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
80 mesh (100%) |
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
1.0% max |
|
RESIDUAL SOLVENTS |
EU2000 |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
|
ARSENIC |
2ppm max |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
| MICROBIOLOGY |
Total Plate Count: 1000 CFU/g max |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |