| TERBINAFINE HYDROCHLORIDE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 91161-71-6 (Base), 78628-80-5 (Hydrochloride) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
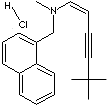
| FORMULA | C21H25N·HCl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 327.89 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Rat LD50 (subcutaneous): > 2gm/kg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Terbinafina; terbinafine hydrochloride; Lamasil; Lamisil; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(e)-N-(6,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)- N-methyl- 1- naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride; N,6,6-Trimethyl-N-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine hydrochloride; ((2E)-6,6-Dimethylhept-2-en-4-yn-1-yl)(methyl)(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)amine; trans-N-(6,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ylyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthylmethylamine hydrochloride; |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
c12c(cccc1cccc2)C[N@@](C\C=C\C#CC(C)(C)C)C.Cl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Allylamine, Anti-infective, Antifungal, Enzyme Inhibitor, Antibiotic, Antimycobacterial. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 195 - 198 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
slightly
soluble | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Terbinafine is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent. It belongs to the family of allylamine structure antifungal agent such as amorolfine, naftifine, butenafine which interferes with biosynthesis of ergosterol needed for the fungal cell membrane. Allylamine antifungal agents are highly lipophilic and are applied topically to the skin, nails, and fatty tissues. Chemically terbinafine is (e)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)- N-methyl- 1- naphthalenemethanamine. Terbinafine hydrochloride is a white to off- white fine crystalline powder; slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in lower alcohol and methylene chloride. Terbinafine is also used as a trypanocidal agent.
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Terbinafine http://www.jornaldepneumologia.com.br/ http://jcm.asm.org/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASSAY |
99.0 - 101.0% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
195 - 198 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IMPURITY |
0.5% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 24/25-28A-37-45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||