| TICARCILLIN DISODIUM | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO | 4697-14-7,
34787-01-4 (parent) 74682-62-5 (disodium salt) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 252-213-5 | |
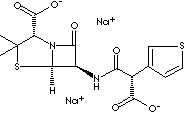
| FORMULA | C15H14N2Na2O6S2 | |
| MOL WT. | 428.38 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Ticarcilina; Ticarcilline; Ticarcillinum; | |
| N-(2-Carboxy-3,3-dimethyl -7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] hept-6-yl)-3-thio- phenemalonamic acid; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6- ((carboxy-3-thienylacetyl)amino)- 3,3- dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2S-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta(S')))-; 6-((Carboxy-3-thienylacetyl)amino)-3,3- dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0) heptane-2-carboxylic acid. | ||
| DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | 6 - 8 | |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Ticarcillin is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic effective against both
gram-negative and gram-positive organisms, derived from penicillin similar to carbenicillin in action. It is derived
from the basic penicillin nucleus, 6-amino-penicillanic acid. The chemical
designation is 6-((Carboxy-3-thienylacetyl) amino)-3,3- dimethyl-7-oxo-4-
thia-1-azabicyclo (3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid. It is used primarily in the treatment of
severe systemic infections, septicemia, and infections of the genitourinary
tract, the respiratory tract, or the soft tissues due to susceptible strains of
bacteria. It should be used only to treat infections by bacteria. It will not
treat viruses, including the flu. Ticarcillin is combined with potassium
clavulanate to maintain the effectiveness against resistance to beta-lactam
antibiotics. Ticarcillin disodium is administered intramuscularly or
intravenously.
Beta-lactamase enzymes are produced by some bacteria and have resistance ability to beta-lactam antibiotics. These enzymes deactivate the antibacterial properties of beta-lactam antibiotics by opening the beta-lactam ring. Beta-lactamase inhibitors have little antimicrobial functions themselves and are combined with an actual beta-lactam antibiotic. Beta-lactamase inhibitors' function is to bind beta-lactamase enzymes to form an inactive molecule so that the actual beta-lactam antibiotic access to the bacterial wall which it destroys. Beta-lactamase inhibitors include clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
passed |
|
| ASSAY | 800 µg/mg (on the anhydrous basis) min | |
| TICARCILLIN CONTENT | 80.0 - 94.0 % (on the anhydrous basis) | |
| BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS | 0.05 EU/mg max | |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+172º ~ +187º | |
|
WATER |
|
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
5kgs
in drum
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||