PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
44 - 46 C
206 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% min
44 - 46 C
MOISTURE
0.5% max
|
|
|
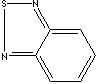
| 2,1,3-BENZOTHIADIAZOLE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 273-13-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 205-985-2 | |
| FORMULA | C6H4N2S | |
| MOL WT. | 136.17 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | Benzo-2,1,3-thiadiazole; 3,4-Benzo-1,2,5-thiadiazole; | |
| Benzisothiadiazole; 2-Thia-1,3-diaza-2H-isoindene; Piazthiole; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT |
44 - 46 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
206 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Benzothiadiazole contains five-membered diunsaturated ring structure fused to benzene ring with two nitrogen atoms at 1,3 position and one sulfur atom at 2 position in the five-membered ring. Thiadiazole and its derivatives are used for biological activities such as antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and antituberculous. But benzothiadiazole is known as an inducer of systemic resistance to diseases rather than direct antifungal or antibacterial activities. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
| MELTING POINT |
44 - 46 C |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 22-24/25 | ||
|
|