4-CHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
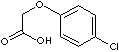
c1(ccc(cc1)Cl)OCC(=O)O
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
soluble in most common organic solvents
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
Google Scholar Search - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
PubChem Compound Summary - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
Local:
Auxin is one of five (or more) major plant hormones (Auxin, Cytokinins,
Gibberellins, Ethylene and Abscisic acid) which affect numerous plant growth processes functions including cell division and elongation, autumnal loss of leaves, and the formation of buds, roots, flowers, and fruit. Auxin action is inhibited by light which is an important role of the growth of stems toward
light (phototropism), against the force of gravity (geotropism) and positively hydrotropic (moisture-seeking). The cells exposed to light don't grow as quickly as those on the shaded side, and thus the plant grows toward the light source. Auxins usually have a ring system with at least one double bond and attached by a side-chain that terminates in a carboxyl group. Indole acetic acid is the exact structure of Auxin activity. Parent compounds of auxin action are;
- Auxins
- 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (CAS RN: 122-88-3)
- (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (CAS RN: 94-75-7)
- 4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (CAS RN: 94-82-6)
- Tris[2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)ethyl] phosphite (CAS RN: 94-84-8)
- 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 120-36-5)
- 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 93-72-1)
- Indole-3-acetic acid (CAS RN: 87-51-4)
- Indole-3-butyric acid (CAS RN: 133-32-4)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetamide (CAS RN: 86-86-2)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (CAS RN: 86-87-3)
- 1-Naphthol (CAS RN: 90-15-3)
- Naphthoxy acetic acid (CAS RN: 120-23-0)
- Naphthenic acid, inorganic salts (potassium, sodium)
- (2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy) Acetic acid (CAS RN: 93-76-5)
- Antiauxins
- Clofibric acid (CAS RN: 882-09-7)
- 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid (CAS RN: 88-82-4)
Cytokinin is a N6-substituted adenines acting as phytohormones such as kinetin, zeatin, 6-isopentenyladenine, benzyl adenine. The principal functions are stimulate cell division in concert with auxin (cytokinesis) and influence the pathway of tissue differentiation (organogenesis). 6-Benzylaminopurine is the first generation synthetic cytokinin which elicits plant growth and development responses setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. Active cytokinin ingredients include:
- Adenine (CAS RN: 73-24-5)
- Adenine Hemisulfate salt (CAS RN: 321-30-2)
- 6-Benzylaminopurine (CAS RN: 1214-39-7(base), 162714-86-5(HCl)
- N-Benzyl-9-(2-tetrahydropyranyl)adenine (CAS RN: 2312-73-4)
- N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N'-phenylurea (CAS RN: 68157-60-8)
- 6-(gamma,gamma-Dimethylallylamino)purine (CAS RN: 2365-40-4)
- 1,3-Diphenylurea (CAS RN: 102-07-8)
- Kinetin (CAS RN: 525-79-1 (base), 177966-68-6 (HCl)
- 1-Phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl) Urea (CAS RN: 51707-55-2)
- Zeatin (CAS RN: 13114-27-7)
- trans-Zeatin (CAS RN: 1637-39-4 (base), 6025-81-6 (HCl))
- trans-Zeatin riboside (CAS RN: 6025-53-2)
Other Plant Growth Regulators include:
- Abscisic acid (CAS RN: 21293-29-8)
- Ancymidol (CAS RN: 12771-68-5)
- Chlorocholine chloride (CAS RN: 999-81-5)
- Daminozide (CAS RN: 1596-84-5)
- 3,6-Dichloro-o-anisic acid (CAS RN: 1918-00-9)
- Gibberellic acid (CAS RN: 77-06-5)
- Gibberellic acid Potassium salt (CAS RN: 125-67-7)
- Gibberellin A4 (CAS RN: 468-44-0 ) and other gibberellins (more than 110 gibberellins are known)
- Glyphosate (CAS RN: 1071-83-6)
- Jasmonic acid (CAS RN: 3572-66-5)
- 1,3,5-Trihydroxybenzene (CAS RN: 108-73-6)
Phenoxy compounds and their alkali or amine salts or esters can be used as growth regulators by aqueous foliar sprays to reduce pre-harvest fruit drop, to increase the proportion of uniform sizes and to increase fruit storage term. Phenoxy compounds, however, may have poor selectivity, and are used as herbicides against broad-leaf weeds rather than growth regulators.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302
P STATEMENTS
P280-P301 + P310
![]()
RISK PHRASES
22
SAFETY PHRASES