| CAS
NO. |
92-69-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
202-179-2 |
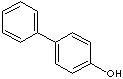
| FORMULA |
C6H5C6H4OH |
| MOL
WT. |
170.21 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2907.19.8000 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral rat LD50;
2000 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
p-Phenylphenol;
1,1'-Biphenyl-4-ol; (1,1-Biphenyl)-4-ol; |
| 4-Hydroxdiphenyl; 4-Hydroxybiphenyl;
Biphenylol; Biphenyl-4-ol; p-Xenol; Orthoxenol; 4-Biphenylol;
p-Xonal; p-Hydroxydipbenyl; Paraxenol; 4-Diphenylol;
4-Phenylphenol; Phenol p-phenyl; Paraxenol; para-Hydroxydiphenyl;
para-Phenylphenol; Other RN: 61840-56-0, 110617-59-9 |
| SMILES |
c1(c2ccccc2)ccc(O)cc1 |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
Phenol, Biphenyl
|
|
EXTRA
NOTES
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white flakes,
mild odor |
| MELTING POINT |
165
- 167 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
307
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
0.7 g/l at 20 C |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
soluble in alkalies, in most organic solvents |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| pKa |
9.55
(Dissociation Constant
at 25 C) |
| log P |
3.2
(Octanol-water) |
| VAPOR
PRESSURE |
1.86E-05 (mmHg at 25 C) |
|
HENRY LAW
CONSTANT |
5.23E-08 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) |
| OH RATE
CONSTANT |
2.73E-11 (cm3/molecule-sec
at 25 C Atmospheric) |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
250
C
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 |
| FLASH
POINT |
165
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS
& GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
|
|
Material
Safety Data Sheet
Google
Scholar Search
PubChem
Compound
Summary
- 4-Phenylphenol
Local:
Phenylphenol is used in formulating biocides and preservatives. It can be used
as a additive for food packaging materails, seed boxes and household goods as a
disinfectant and fungicide. Phenylphenol is used to
manufacture germicide, fungicide, rubber chemicals and dyes.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white flakes |
|
ASSAY
|
98.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
165
- 167 C |
|
MOISTURE
|
0.1%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
Not regulated
|
| SAFETY
INFORMATION |
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW
|
Causes skin irritation. Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause
long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. May cause
eye and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Skin.
|
|
GHS
|
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS
|
 
|
|
HAZARD
STATEMENTS
|
H315: Causes skin irritation
H319: Causes serious
eye irritation
H335: May cause respiratory irritation
H411:
Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
|
|
PRECAUTIONARY
STATEMENTS
|
P273: Avoid release to the environment
P280: Wear
protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection
P302+
P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water
P305
+ P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for
several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do.
Continue rinsing
|
|
EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
HAZARD
CODES |
 Xi
Irritant Xi
Irritant
|
|
RISK PHRASES
|
36/37/38: Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
51/53:
Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects
in the aquatic environment.
|
|
SAFETY
PHRASES
|
37: Wear suitable gloves.
61: Avoid release to
the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets.
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF BIPHENYL |
|
Biphenyl (also
called Diphenyl, but exactly one of two compounds. The other is o-phenylphenol,
used to prevent the growth of moulds ) is an aromatic hydrocarbon; molecule
structure is composed of two six-sided carbon rings connected at one carbon site
on each ring. Pure biphenyl is a toxic colourless crystalline solid with a
pleasant odour; melting point 70 C, boiling point 255 C, which gives plates or
monoclinic prismatic crystals; it is insoluble in water but soluble in ordinary
organic solvents. It is directly used in the preservation of citrus fruits as a
fungistat in transportation containers. It is a raw material for polychlorinated
diphenyls (PCB) in which chlorine replaces hydrogen in biphenyls. There are 209
chlorinated isomers of biphenyl theoretically. But PCBs are referred to the
biphenyl compounds with one to ten chlorine substitutions. PCBs are used
heat-transfer agents and as electric insulators that block the flow of electric
current across in electrical equipments. They are known as environmental
pollution materials which are accumulated in animal tissues and cause toxic
effects including carcinogenesis. Biphenyl is used as an intermediate for the
production of a wide range of organic compounds (e.g. emulsifiers, optical
brighteners, crop protection products, plastics), as a heat transfer medium
alone or with diphenyl ether in heating fluids, as a dyestuff carrier for
textiles and copying paper and as a solvent in pharmaceutical production. Aminodiphenyls
are used as rubber
antioxidants and intermediates for the synthesis of
organic compounds ( azo dyes and pharmaceuticals). Biphenyl derivatives
are used as an intermediate for the synthesis of organic
compounds including pharmaceuticals, antifungal agents,
optical
brightening agents and dyes.
Biphenyl compounds also used in luminescence
chemistry, spectrophotometric analysis, molecular
chemistry, and as a stating material
for organometallic-complexes. |
|
PRICE
INFORMATION |
|
|



![]() Xi
Irritant
Xi
Irritant