PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
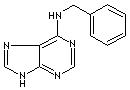
c12c(NCc3ccccc3)ncnc1nc[nH]2
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
- Auxins
- 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (CAS RN: 122-88-3)
- (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (CAS RN: 94-75-7)
- 4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (CAS RN: 94-82-6)
- Tris[2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)ethyl] phosphite (CAS RN: 94-84-8)
- 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 120-36-5)
- 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 93-72-1)
- Indole-3-acetic acid (CAS RN: 87-51-4)
- Indole-3-butyric acid (CAS RN: 133-32-4)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetamide (CAS RN: 86-86-2)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (CAS RN: 86-87-3)
- 1-Naphthol (CAS RN: 90-15-3)
- Naphthoxy acetic acid (CAS RN: 120-23-0)
- Naphthenic acid, inorganic salts (potassium, sodium)
- (2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy) Acetic acid (CAS RN: 93-76-5)
- Antiauxins
- Clofibric acid (CAS RN: 882-09-7)
- 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid (CAS RN: 88-82-4)
Cytokinin is a N6-substituted adenines acting as phytohormones such as kinetin, zeatin, 6-isopentenyladenine, benzyl adenine. The principal functions are stimulate cell division in concert with auxin (cytokinesis) and influence the pathway of tissue differentiation (organogenesis). 6-Benzylaminopurine is the first generation synthetic cytokinin which elicits plant growth and development responses setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. Active cytokinin ingredients include:
- Adenine (CAS RN: 73-24-5)
- Adenine Hemisulfate salt (CAS RN: 321-30-2)
- 6-Benzylaminopurine (CAS RN: 1214-39-7(base), 162714-86-5(HCl)
- N-Benzyl-9-(2-tetrahydropyranyl)adenine (CAS RN: 2312-73-4)
- N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N'-phenylurea (CAS RN: 68157-60-8)
- 6-(gamma,gamma-Dimethylallylamino)purine (CAS RN: 2365-40-4)
- 1,3-Diphenylurea (CAS RN: 102-07-8)
- Kinetin (CAS RN: 525-79-1 (base), 177966-68-6 (HCl)
- 1-Phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl) Urea (CAS RN: 51707-55-2)
- Zeatin (CAS RN: 13114-27-7)
- trans-Zeatin (CAS RN: 1637-39-4 (base), 6025-81-6 (HCl))
- trans-Zeatin riboside (CAS RN: 6025-53-2)
Other Plant Growth Regulators include:
- Abscisic acid (CAS RN: 21293-29-8)
- Ancymidol (CAS RN: 12771-68-5)
- Chlorocholine chloride (CAS RN: 999-81-5)
- Daminozide (CAS RN: 1596-84-5)
- 3,6-Dichloro-o-anisic acid (CAS RN: 1918-00-9)
- Gibberellic acid (CAS RN: 77-06-5)
- Gibberellic acid Potassium salt (CAS RN: 125-67-7)
- Gibberellin A4 (CAS RN: 468-44-0 ) and other gibberellins (more than 110 gibberellins are known)
- Glyphosate (CAS RN: 1071-83-6)
- Jasmonic acid (CAS RN: 3572-66-5)
- 1,3,5-Trihydroxybenzene (CAS RN: 108-73-6)
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benzyladenine
http://www.hos.ufl.edu/
In
traditional in vitro culture, explants grow enclosed in a non-ventilated
vessel at high relative humidity with phytohormones continuously
present and sucrose as the main energy source. Under such conditions
explant growth is far from normal. In this paper, explants of Actinidia
deliciosa were cultured in MS medium supplemented with sucrose,
benzyladenine and gibberellic acid under autotrophic conditions
in glass boxes flushed with air enriched with 600 μl l–1 CO2 for
the first 20 days and then transferred to MS medium until the end
of the culture period. The effect of benzyladenine was assayed in
two regimes of application: in cultures for 20 days in the medium
or only 24 h in the presence of benzyladenine with the aim of improving
shoot proliferation and acclimatisation. The longest explants were
those grown under ventilation and pulsed for 24 h with benzyladenine.
These explants also rooted spontaneously, whereas those grown with
continuous benzyladenine under ventilation or without ventilation
grew and rooted poorly. The highest amount of endogenous isoprenoid
cytokinins were found in the longest explants grown under ventilation
and pulsed for 24 h with benzyladenine; under these conditions zeatin
riboside represented two thirds of the entire cytokinin pool. These
explants presented the highest amount of indole-3-acetic acid, while
abscisic acid content was high in explants cultured under non-ventilated
conditions. No differences were observed between explants cultured
under ventilation regardless of their exposure to benzyladenine.
The longest explants, which also performed best in acclimatisation,
also presented a high indole-3-acetic to abscisic acid ratio.
http://www.hcs.ohio-state.edu/
There are a number of naturally occuring cytokinins all related to the
nucleotide adenine. They can occur as the free base
or as a riboside. Synthetic cytokinins include benzyladenine and kinetin.
Cytokinins are used in tissue culture media, and for growth control in
fruit.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
PRICE INFORMATION